Figure 7.
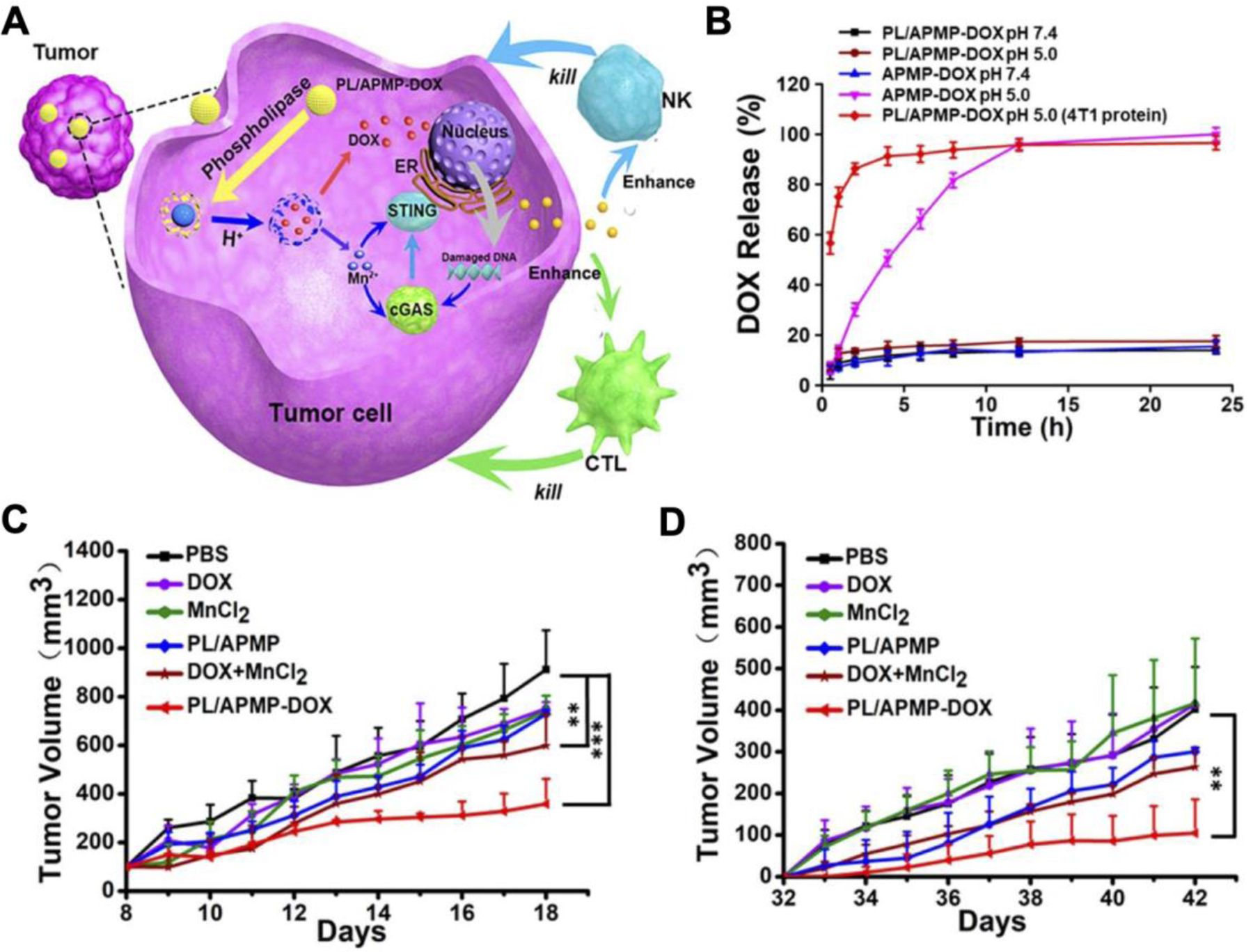
Manganese nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin (DOX) for synergistic immunotherapy against 4T1 breast cancer. A) The degradation of DOX-loaded amorphous porous manganese phosphate nanoparticles coated with phospholipid (PL/APMP-DOX) is facilitated by phospholipase within tumor cells. DOX causes damaged DNA to release from the nucleus, while manganese ions (Mn2+) facilitate STING activation to promote immune responses mediated by natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). B) DOX is rapidly released at low pH and in the presence of phospholipase, which are significantly upregulated in cancerous cells. C,D) Intravenous treatment with PL/APMP-DOX reduces growth in both the primary tumor (C) and a distant secondary tumor (D) inoculated post-treatment. Reproduced with permission (Hou et al., 2020). Copyright 2020, American Chemistry Society.
