Figure 5. The contents of lutein, zeaxanthin, and β-carotene detected in the RPE/choroids of the ApoA-I−/−/Bco2−/− mice and the Bco2−/− mice by HPLC.
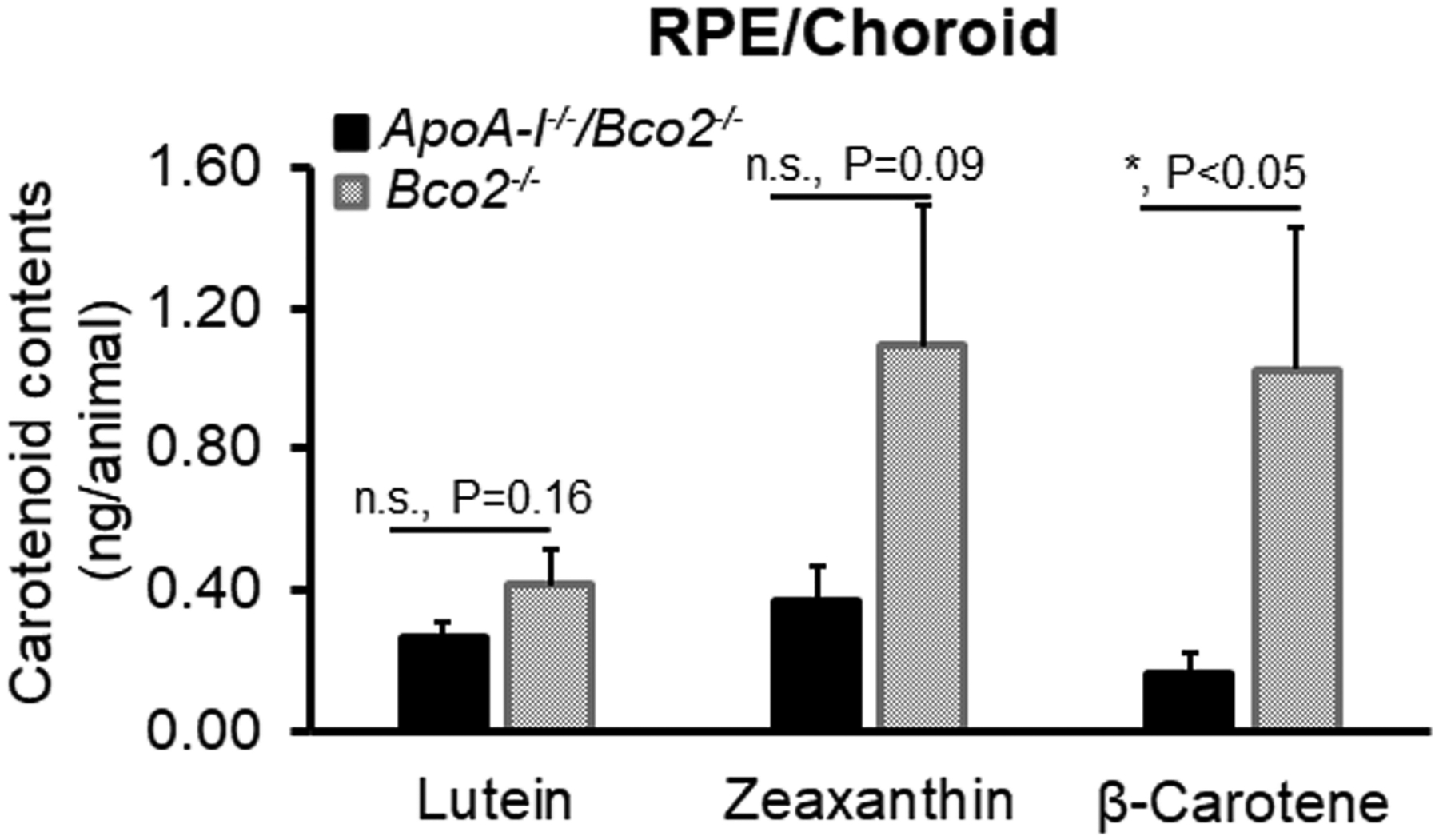
The levels of all three carotenoids in the RPE/choroids of ApoA-I−/−/Bco2−/− mice were decreased relative to the Bco2−/− mice. It also showed that ApoA-I deficiency resulted in more reduction of zeaxanthin and β-carotene than lutein, suggesting that zeaxanthin and β-carotene are transported to RPE/choroids by HDL. In contrast, lutein is probably delivered by LDL. The ratio of lutein:zeaxanthin:β-carotene is 1: 2.6: 2.5 in the Bco2−/− mice, while it becomes 1.0: 1.4: 0.6 in the ApoA-I−/−/Bco2−/− mice. Carotenoids were extracted from four RPE/choroid samples pooled from twenty ApoA-I−/−/Bco2−/− double knockout mice and four RPE/choroid samples pooled from twenty Bco2−/− mice (5 pairs of RPE/choroids/sample). *, P<0.05. Error bars represent standard deviation.
