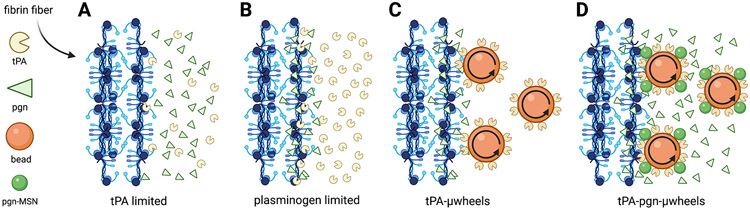
Fig. 1:
A) The rate-limiting steps of fibrinolysis include the transport to a clot and binding of tPA to fibrin fibers at low tPA concentrations. B) At sufficiently high tPA concentrations, its substrate plasminogen (pgn), becomes the limiting factor in fibrinolysis. C) These rate-limiting steps are overcome using magnetically powered μwheels, superparamagentic beads (orange spheres) that self-assemble in rotating magnetic fields. When μwheeels are coupled to tPA (tPA-μwheels) they accumulate at the clot interface leading to high tPA concentrations and plasminogen limited fibrinolysis. D) By attaching plasminogen releasing nanoparticles (green spheres) to μwheels (tPA-pgn-μwheels) co-delivery of both enzyme and substrate are achieved yielding fibrinolysis rates that overcomes plasminogen-limited fibrinolysis.