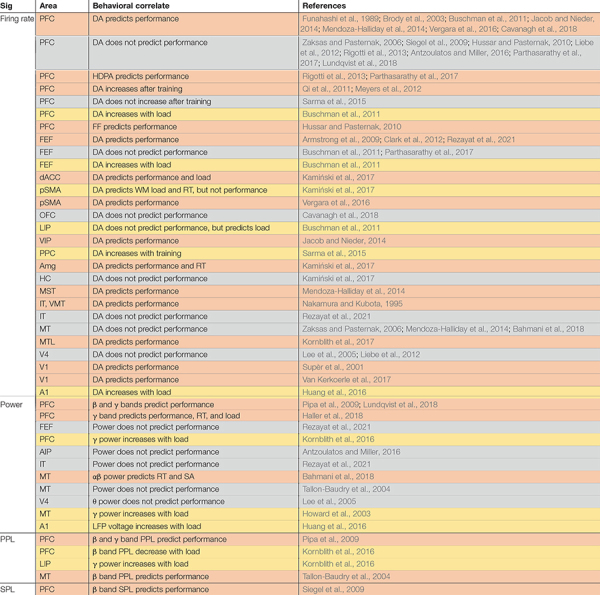
TABLE 1.
Neural signatures of working memory (WM) within areas and their relationship to behavior.
|
Studies are first grouped according to the neural signature being studied during WM maintenance (Sig). Firing rate measures are usually based on single neurons, whereas LFP power, spike-phase locking (SPL), and phase-phase locking (PPL) are population-level measures. SPL measures the regularity of spike timing relative to the phase of a particular LFP oscillatory frequency. Phase-phase locking (PPL) measures synchronization between the same frequency oscillation at two sites. The second column groups studies by the area being recorded from Area. The effect of WM and its relationship between this modulation and the animal’s behavior is noted (Behavioral correlate). Each row summarizes related studies (References). Coloring indicates whether the signature was correlated with performance [percent correct, reaction time (RT), or saccade accuracy (SA); orange] or some other aspect of behavior on a WM task (load, training; yellow); rows in gray showed no correlation, blue showed negative correlation. Studies which report data for more than one area may be listed multiple times. Note that in humans, ECoG measurements of LFPs biased are toward temporal and frontal sites as a result of clinical considerations (Tallon-Baudry et al., 2001; Howard et al., 2003; Axmacher et al., 2008, 2010; van Vugt et al., 2010; Khursheed et al., 2011; Maris et al., 2011; van der Meij et al., 2012; Noy et al., 2015; Kambara et al., 2017, 2018; Myroshnychenko et al., 2017; Ni et al., 2017; Johnson et al., 2018a,b; Zhang et al., 2018; Alagapan et al., 2019b; Gehrig et al., 2019; Boran et al., 2020). Sx, signature; PFC, prefrontal cortex; lPFC, lateral PFC; dACC, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex; pSMA, pre supplementary motor area; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; FEF, frontal eye field; LIP, lateral intraparietal; VIP, ventral intraparietal; PPC, posterior parietal cortex; HC, hippocampus; Amg, amygdala; MT, middle temporal; VMT, ventromedial temporal; MST, medial superior temporal; MLT, medial temporal lobe; IT, inferior temporal; FR, firing rate; RT, reaction time; FF, fano factor; PPL, phase phase locking; SPL, spike phase locking; DA, delay activity of single neurons; HDPA, high dimension population activity. Frequency bands (θ, α, β, and γ) are reported based on the definitions in each reference; exact cutoffs may vary, but roughly correspond to 4–8, 8–15, 15–35, and 35–80 Hz, respectively.
