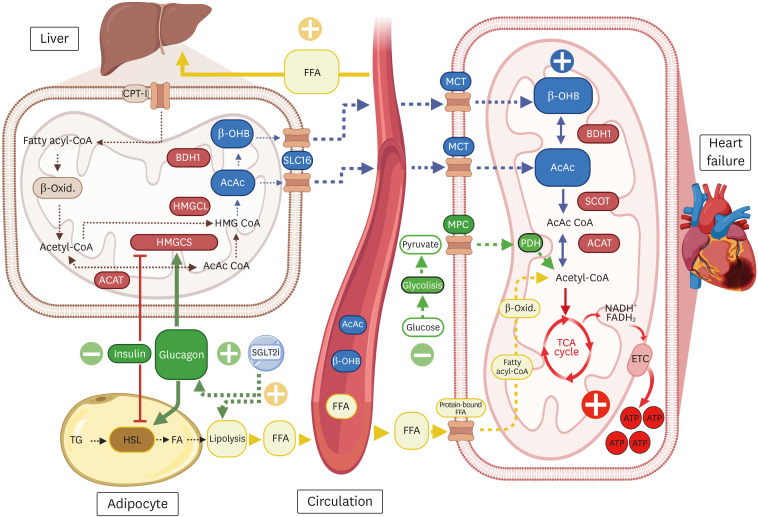
Fig. 1. Energy production through SGLT2 inhibitors and ketone bodies.
By reducing plasma glucose levels due to increased insulin sensitivity and enhanced gluconeogenesis, the mobilization of deposits of FFA to the liver increases secondary to HSL stimulation. In the liver, FFA are oxidized, generating acetyl-CoA. Two acetyl-CoA derived from FFA are used to produce acetoacetyl-CoA by a thiolase reaction; another acetyl-CoA is condensed into acetoacetyl-CoA by HMGCS2 (this synthase is inhibited by insulin and stimulated by glucagon). After HMGC, it is lysed by HMGCL, generating AcAc, which is oxidized by BDH1 to generate β-OHB. The latter two substances are probably released into circulation through SCL16. Myocytes take up ketone bodies through MCT. β-OHB is converted to AcAc again to be metabolized to acetoacetyl-CoA by SCOT; subsequently, through ACAT, acetyl-CoA is generated to enter the TCA cycle and produce ATP. The image was created with BioRender.com.
ACAT, acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase; AcAc, acetoacetate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BDH1, β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase-1; CPT-I, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; ECT, electron transport chain; FA, fatty acid; FFA, free fatty acids; HMGCS2, 3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2; HMGC, 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl-CoA; HMGCL, 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase; MCT, monocarboxylate transporter; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; SCL16, solute carrier 16A family members; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 Inhibitors; SCOT, succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid coenzyme A transferase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TG, triglyceride; β-OHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; β-Oxid, β-oxidation.