Figure 1. CT axial, MRI T2 axial, CT sagittal and MRI T1 post-gadolinium sagittal images at 3–4 month intervals of a 16-month-old HIV-infected female with stage III tuberculous meningitis.
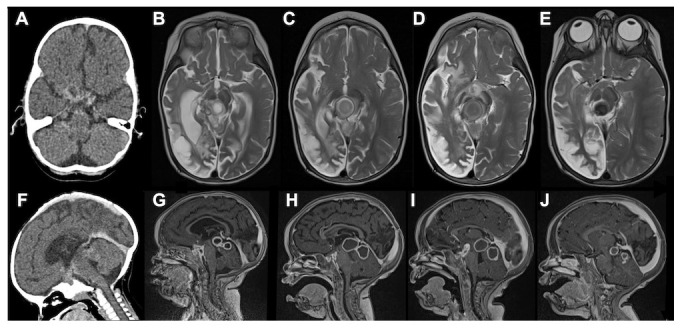
The initial computed tomography (CT) axial and sagittal scans ( A, F) showed a large right sided middle cerebral artery infarction, hydrocephalus as well as multiple small rim-enhancing foci in the prepontine cisterns. After three months of anti-TB and two months of anti-retroviral therapy, they presented with a depressed level of consciousness. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2 axial ( B) and MRI T1 post-gadolinium sagittal ( G) demonstrated multiple TB abscesses in the interpeduncular, prepontine and chiasmic cisterns (paradoxical HIV related TB IRIS) as well as right cerebral hemisphere spongiotic changes (old infarction). Thalidomide was initiated following a poor response to one week of high dose corticosteroids. This resulted in rapid improvement in the level of consciousness, gradual decrease in the size of the TB abscesses and loss of T2 signal (i.e. inflammation), which is a marker of cure as it represents gradual calcification ( C– E & H– J). We confirm that we have obtained consent to use images from the parent/guardian of the patient included in this presentation. Permission was obtained in the form of informed written consent.
