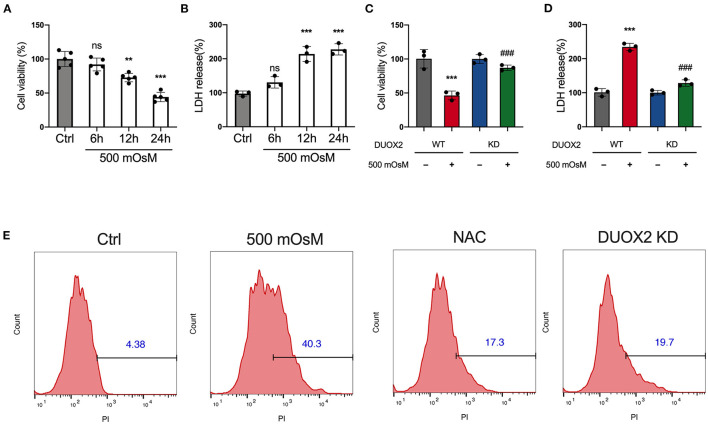
Figure 4.
Ablation of DUOX2 inhibits hyperosmolarity-induced cell death. HCE cells were treated with 500 mOsM or normal culture medium (Ctrl) for 6, 12, and 24 h. (A) Changes in cell viability were determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assay. (B) Changes in LDH levels were monitored by LDH assay. HCE cells were transfected with control siRNA (WT) or DUOX2 siRNA (KD) for 24 h and then treated with 500 mOsM or normal culture medium (ctrl) for 24 h. (C) Changes in cell viability were determined by CCK8 assay. (D) Changes in lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were monitored by LDH assay. (E) HCE cells were transfected with DUOX2 siRNA (DUOX2 KD) for 24 h and cultured in hyperosmotic medium (500 mOsM) for 18 h. Control siRNA transfected HCE cells were exposed to 500 mOsM and co-treated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or left untreated (Ctrl). Positive percentage of propidium iodide (PI) staining was monitored by flow cytometry. The data shown are representative of three or more independent experiments (mean ± SD). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. untreated controls; ###p < 0.001 vs. 500 mOsM(+) DUOX2 KD(–).