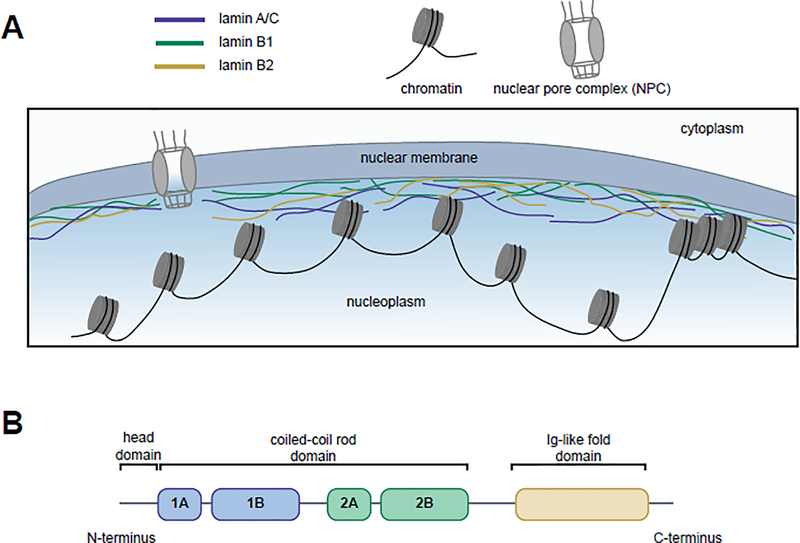
Figure 1. Lamins’ localization to the nuclear periphery and functional domains.
(A) The human lamins, lamin A/C (blue), lamin B1 (green), and lamin B2 (yellow), assemble into a network at the inner nuclear periphery where they serve to maintain nuclear shape and interact with both euchromatic and heterochromatic regions of DNA. (B) Lamins have three domains: a head domain, a coiled-coil rod domain (composed of four sub-domains) that mediates interactions with other lamina proteins, and an Ig-like fold domain that mediates interactions with non-lamina proteins.