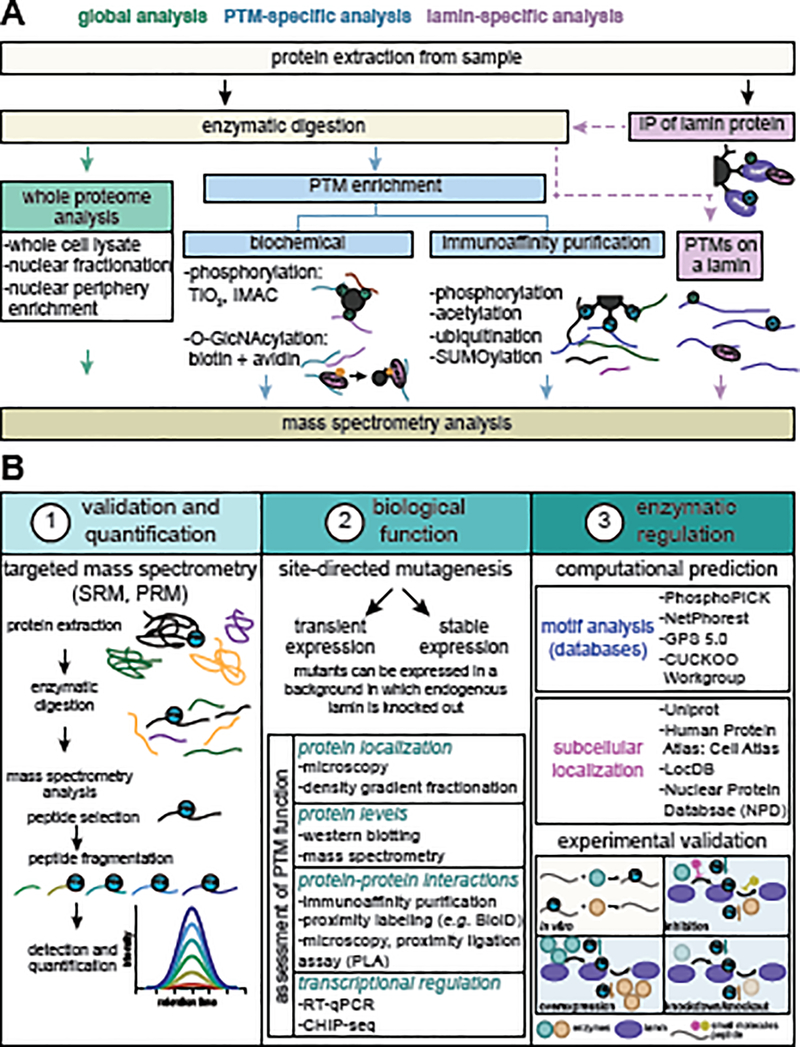
Figure II. Methods to detect and functionally characterize lamin PTMs.
(A) Lamin PTMs can be identified by MS using several experimental workflows, including whole proteome analyses (green), PTM-specific enrichment by biochemical or immunoaffinity purification methods (blue), or lamin-specific enrichment by immunoaffinity purification (IP) of a particular lamin (purple). (B) Considerations when characterizing lamin PTMs are (1) validation and quantification, (2) determination of biological function, and (3) assessment of enzymatic regulation. Targeted MS, including selected reaction monitoring (SRM) and parallel reaction monitoring (PRM), provides the means for confirming and accurately quantifying the levels of a site-specific PTM. Biological function can be determined by employing site-directed mutagenesis of the lamin of interest combined with functional assays that test different aspects of lamin biology (examples of functions and experimental techniques are listed). As many enzymes may regulate the same PTM, employing motif and subcellular localization computational analyses (examples of databases/tools are listed) can narrow the focus on which enzyme(s) may work on a particular PTM. The ability of the enzyme(s) to modify that site can then be tested using in vitro (tan) and cell culture and in vivo experiments (blue). Examples of the consequences on PTM levels of an enzyme that adds (teal) or removes (orange) a given PTM are shown.