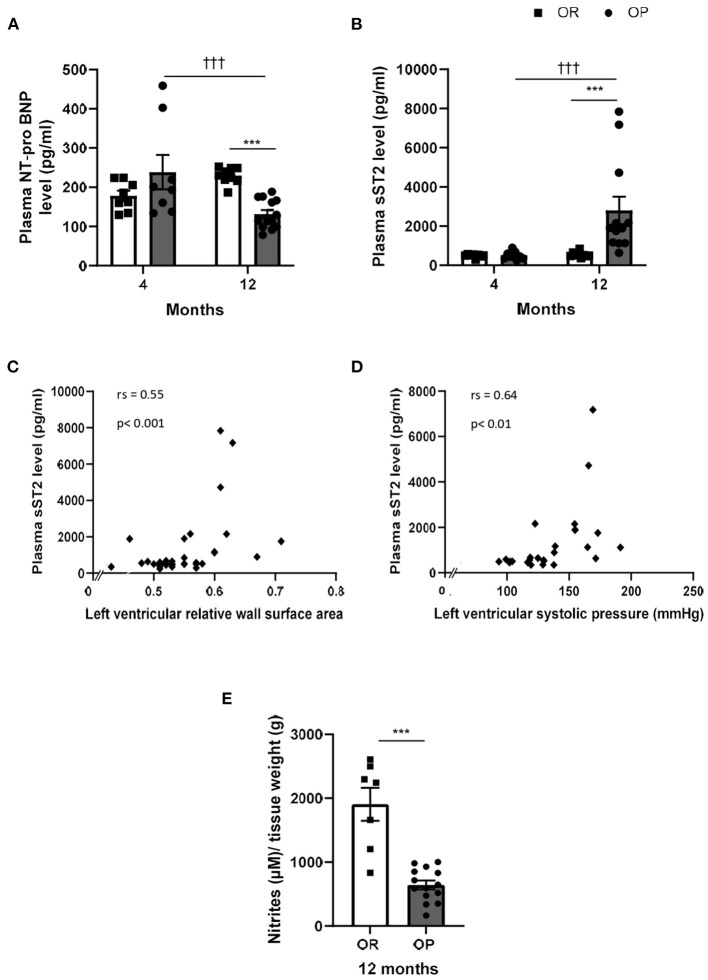
Figure 5.
Plasma cardiac biomarkers in high-fat diet-fed obesity-prone (OP) and normal chow-fed obesity-resistant (OR) rats after 4 and 12 months. Plasma levels of N-Terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide [NT-proBNP; (A)] and soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 [sST2; (B)] in high-fat diet-fed obesity-prone (OP; black bars) vs. normal chow-fed obesity-resistant rats (OR; white bars) at 4 and 12 months. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8–14 rats per group). ***p < 0.001, high-fat diet in obesity-prone (OP) vs. normal chow in obesity-resistant (OR) rats; †††p < 0.001 4- vs. 12-month high-fat diet in obesity-prone (OP) rats. Correlations between plasma soluble ST2 levels and left ventricular structure and hemodynamic parameters, including left ventricular relative surface area (C) and left ventricular systolic pressure [LVSP; (D)] respectively. Data of all experimental groups and both 4- and 12-month protocol duration were gathered and analyzed together using a non-parametric Spearman's rank correlation coefficient analysis. Concentration of nitrites/NO (E) in supernatants of endothelium-intact thoracic aortic rings collected in 12-month high-fat diet-fed obesity-prone rats (OP; black bars) vs. normal chow-fed obesity resistant rats (OR; white bars) incubated during one hour with Krebs solution. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 9–14 rats per group). ***p < 0.001 high-fat diet in obesity-prone (OP) vs. normal chow in obesity-resistant (OR) rats.