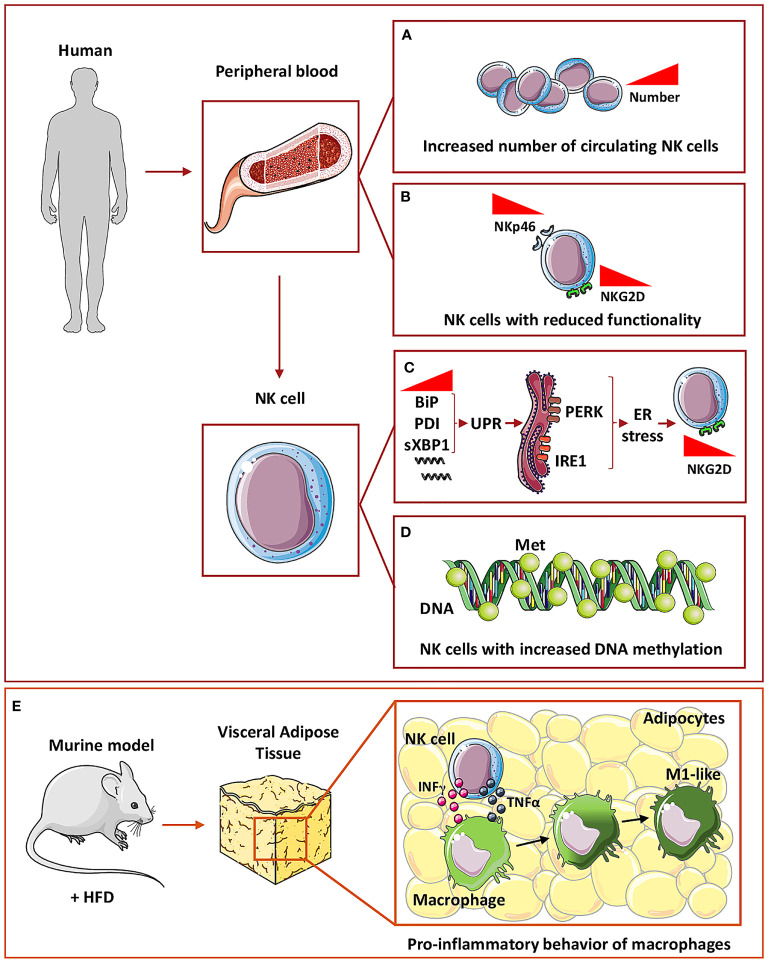
Figure 2.
NK cells in Type 2 diabetes. In humans, circulating NK cells in T2D subjects have been found to increase in number (A) but with decreased expression of both NKp46 and NKG2D activation markers, thus showing a reduced functionality (B). At the molecular level, circulating NK cells in T2D showed an increased mRNA expression of BiP, PDI, and sXBP1, a marker of unfolded protein response (UPR) which in turn is related to ER stress-activated by PERK and IRE1 sensors (C). These mechanisms are related to NKG2D down-modulation in circulating NK cells (C). In addition, NK cells showed an increased general DNA methylation (D). To mimic T2D mice are fed with high fat diet (HFD) (E) and within visceral adipose tissue, NK cells through IFNγ and TNFα release can induce macrophages polarization toward a pro-inflammatory M1-like phenotype thus promoting inflammation (E).