Figure 1. Combination of gemfibrozil and retinoic acid (GFB-RA) enhances Aβ uptake in mouse primary astrocytes.
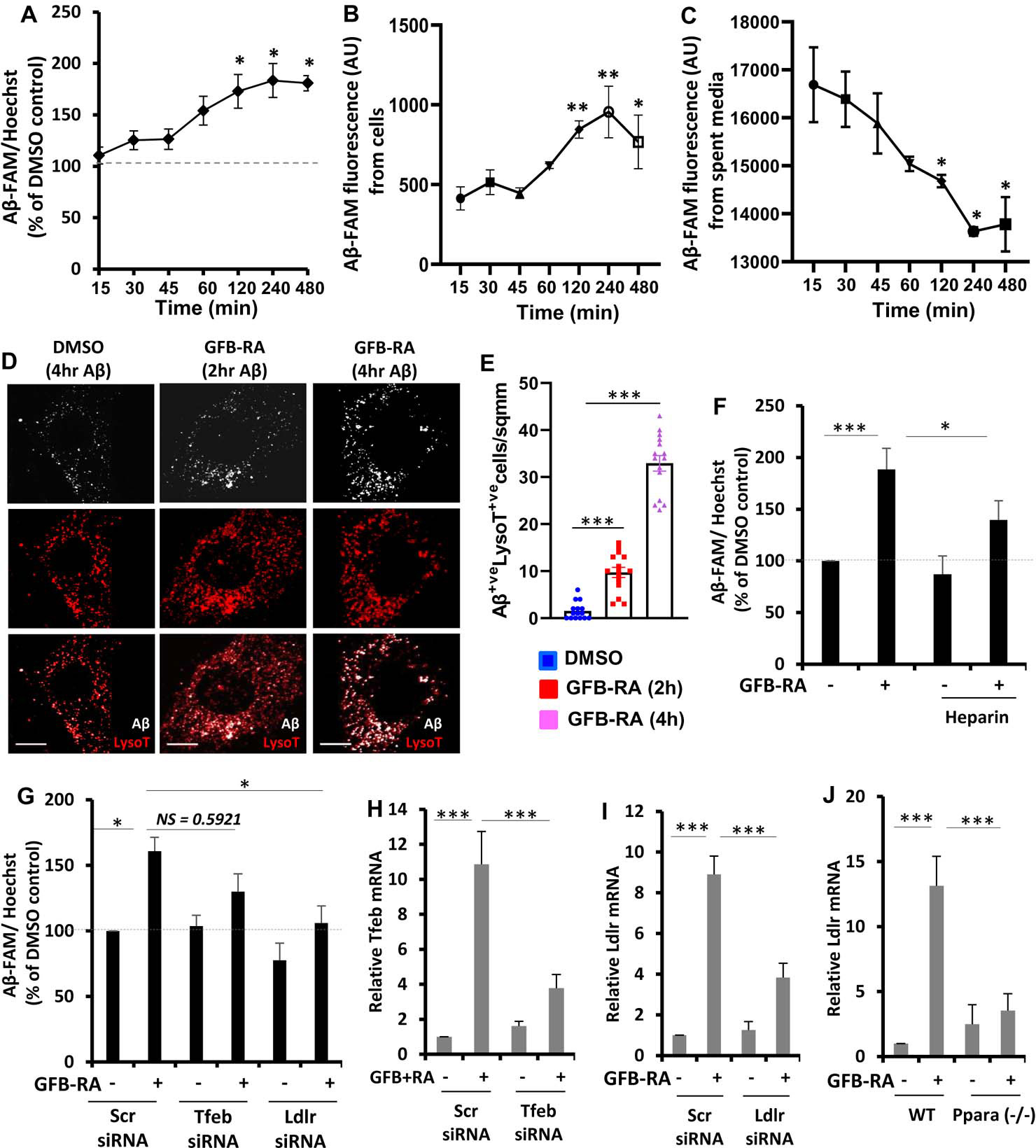
(A) Aβ uptake assay in mouse primary astrocytes were cultured for 24 hours with GFB-RA [GFB (10 μM) + RA (0.2 μM)], followed by 500 nM FAM-tagged Aβ1–42 for a further 15 min to 8 hours. Data are shown as a percent change compared to DMSO-treated controls. (B and C) The fluorescence of FAM-Aβ was monitored over time in the primary astrocytes and media described in (A). (D and E) Mouse primary astrocytes treated with GFB-RA were incubated with 500nM HF-Aβ1–42 and 75 nM Lysotracker Red and observed under microscope. Scale bar = 20 μm. Aβ+Lyso-T+ puncta were counted from 15 astrocytes from three independent experiments. (F) Mouse primary astrocytes were treated with DMSO or GFB-RA, followed by treatment with diluent of heparin (100 μg/ml) and further incubated in 500 nM FAM-Aβ for 4 hours. Aβ uptake assay was performed, and data is shown as percentage change with respect to untreated control. (G) Mouse primary astrocytes were transfected with scrambled siRNA, Tfeb siRNA or Ldlr siRNA, treated with GFB-RA, followed by incubation in 500 nM FAM-Aβ for 4 hours. Data from Aβ uptake assay is represented as percentage change with respect to DMSO and scrambled siRNA controls. (H and I) Real-time PCR was performed to measure the efficacy of siRNA silencing of Tfeb and Ldlr. (J) Wild-type (WT) and Ppara−/− astrocytes were treated with GFB-RA for 4 hours followed by monitoring the mRNA expression of LDLR by real-time PCR. All data are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, each in duplicate. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, and NS denotes not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
