Figure 4. Oral administration of the combination of gemfibrozil and retinoic acid (GFB-RA) activates lysosomal biogenesis in vivo in the hippocampus of 5XFAD mice.
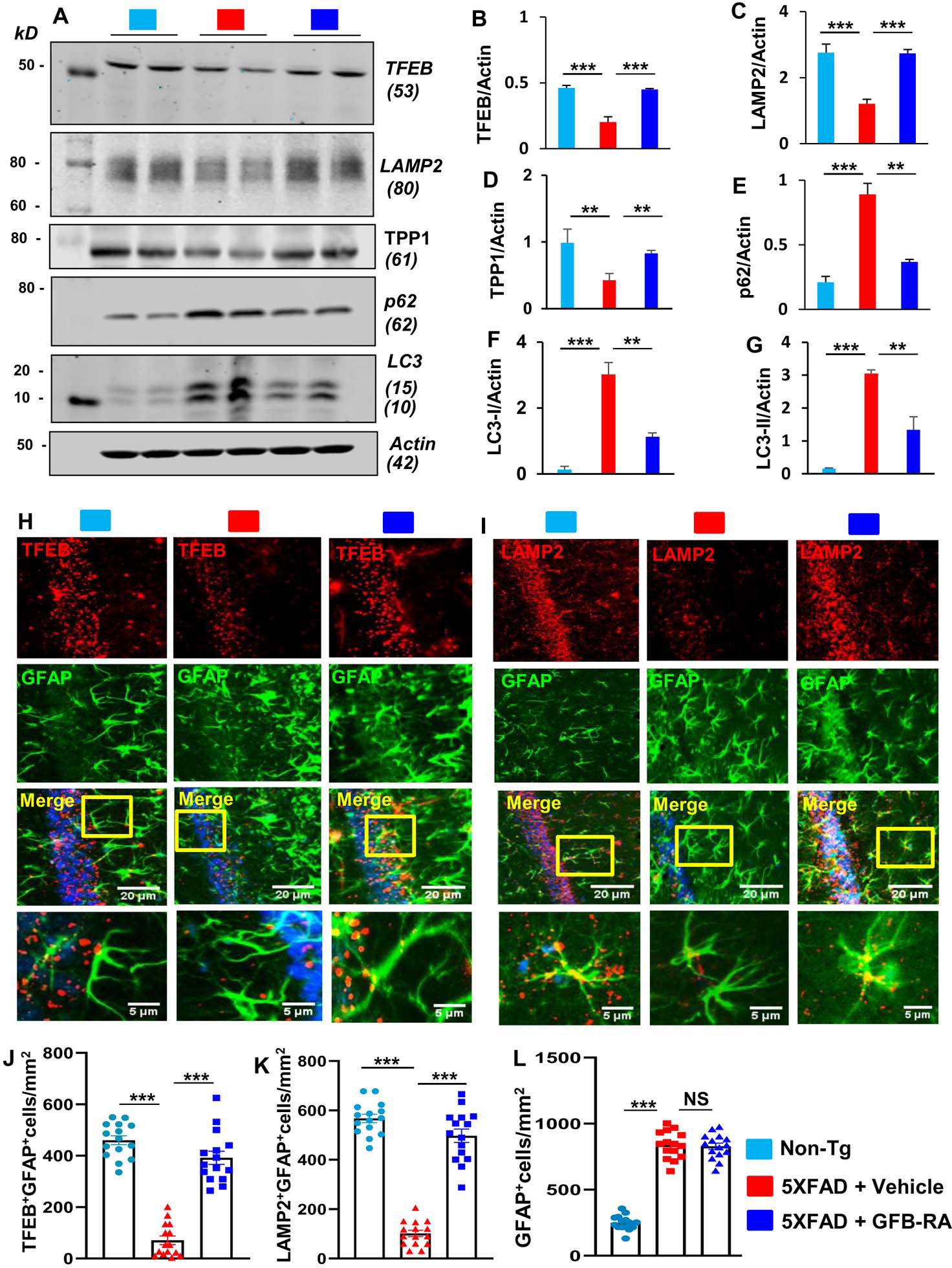
(A to G) Six-month-old 5XFAD mice (n=5/group in two independent experiments) were orally administered with GFB-RA [the combination of gemfibrozil (8 mg/Kg/day) and retinoic acid (150 IU/day)] for two months. The control group of 5XFAD mice received 0.5% methylcellulose as vehicle. Label color code: bottom right. Hippocampal protein homogenates from these mice were then subjected to Western blotting for protein expression of TFEB, LAMP2, TPP1, p62, and LC3 (A). Densitometry analysis of each (B to G) was measured with ImageJ, normalized to that of actin, and presented as relative to control. Data are mean ± SEM of five mice per group. (H to L) Hippocampal sections of mice described in (A) were double-labeled for either TFEB and GFAP (H) or LAMP2 and GFAP (I). Label color code: bottom right; scale bars as marked. TFEB+GFAP+ (J), LAMP2+GFAP+ (K) and GFAP+ (L) cells were counted in one section (3 images per section) of each of five mice per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, and NS denotes not significant by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
