Fig. 6. Dietary methionine restriction augments the antitumor effects of auranofin in a metastatic TNBC mouse model.
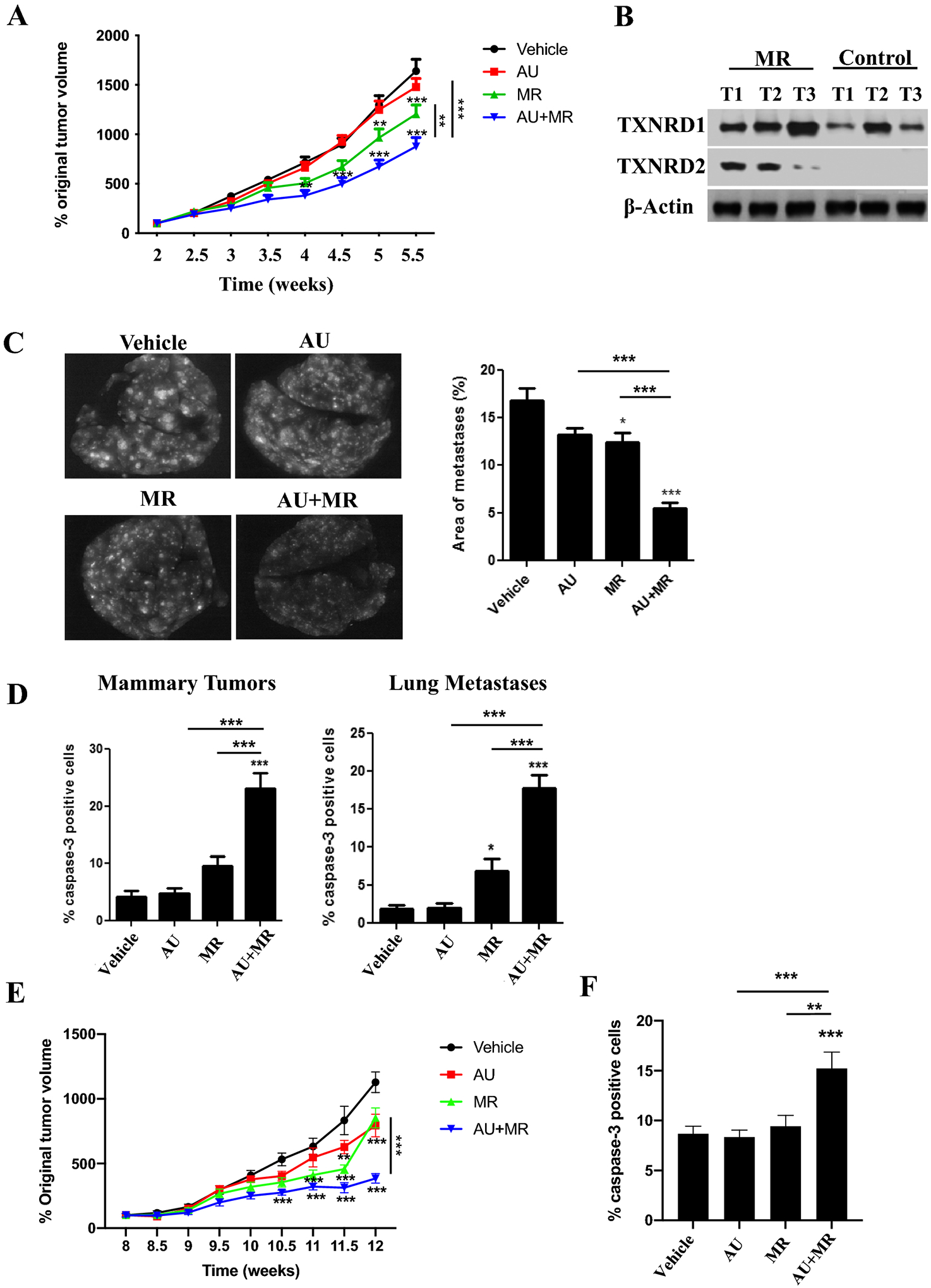
Female NSG mice with GILM2-mCherry mammary tumors (two per mouse, A-D) or PDX TNBC tumors (E-F) were randomly assigned to one of four treatment groups (10 mice per group): control diet plus vehicle, control diet plus auranofin (10 mg/kg daily), MR diet plus vehicle, or MR diet plus auranofin (10 mg/kg daily). The diets were started 2.5 (GILM2) or 8 (PDX) weeks after tumor injection and were continued throughout the treatment period. A, Percentage original GILM2 mammary tumor volume at 2.5 weeks in each group (mean ± SEM, n = 10 mice per group). B, Immunoblot of TXNRD1 and TXNRD2 expression in GILM2 mammary tumors from mice on the control or MR diet. C, Representative images of resected whole lungs at autopsy visualized by fluorescence microscopy in GILM2 model. The percentage of the surface area occupied by fluorescent lung metastases (mean ± SEM, n = 10 mice per group) is indicated. D, The percentage active caspase-3-positive tumor cells in GILM2 mammary tumors (left panel) or GILM2 lung metastases (right panel) after treatment (mean ± SEM, n = 3 tumors per group). E, Percentage original PDX tumor volume at 8 weeks in each group (mean ± SEM, n = 10 mice per group). F, The percentage active caspase-3-positive tumor cells in primary PDX mammary tumors. In all panels, *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated mice or the indicated comparison
