Figure 2: PAM knockout mice.
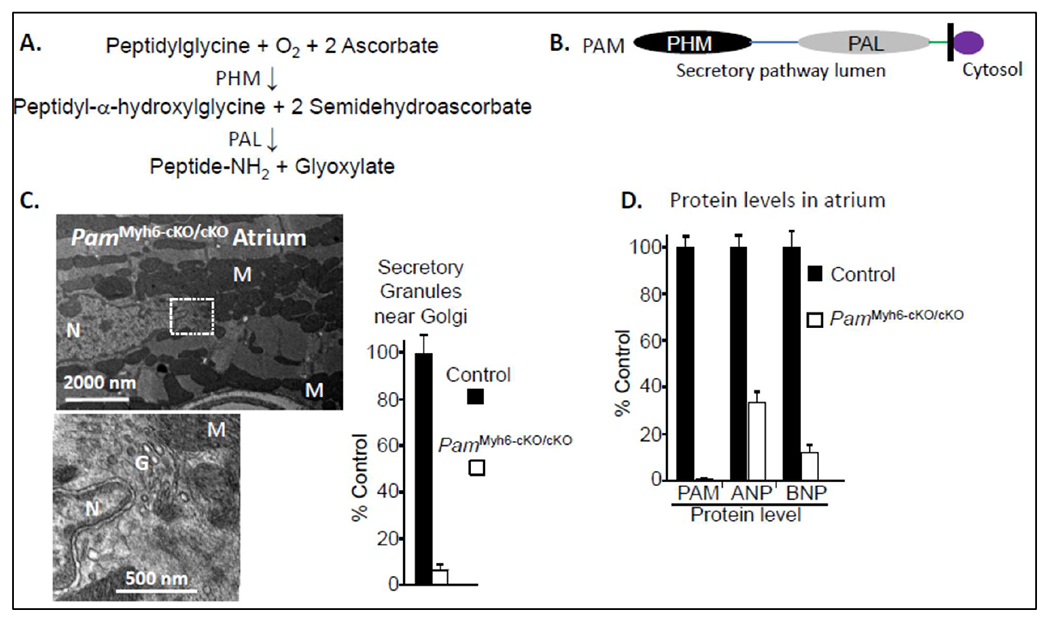
The reaction catalyzed by PAM is outlined (A), along with the major form of PAM in humans (B) and its two enzymatic domains, PHM and PAL (peptidylglycine a-hydroxylating monooxygenase and peptidyl-a-hydroxyglycine a-amidating lyase; E.C. 1.4.17.3 and 4.3.2.5). C. Transmission electron micrographs of the PamMyh6-cKO/cKO adult atrium; secretory granules are rarely seen near the peri-nuclear Golgi or elsewhere. Quantitative data comparing the number of Golgi-localized secretory granules observed in control vs. PamMyh6-cKO/cKO atria revealed a nearly 20-fold decrease (Figure 1A). D. Immunoblot analyses of adult atria established near-total ablation of PAM and major loss of proANP and proBNP in PamMyh6-cKO/cKO atrium. Data replotted from [13].
