FIG. 6.
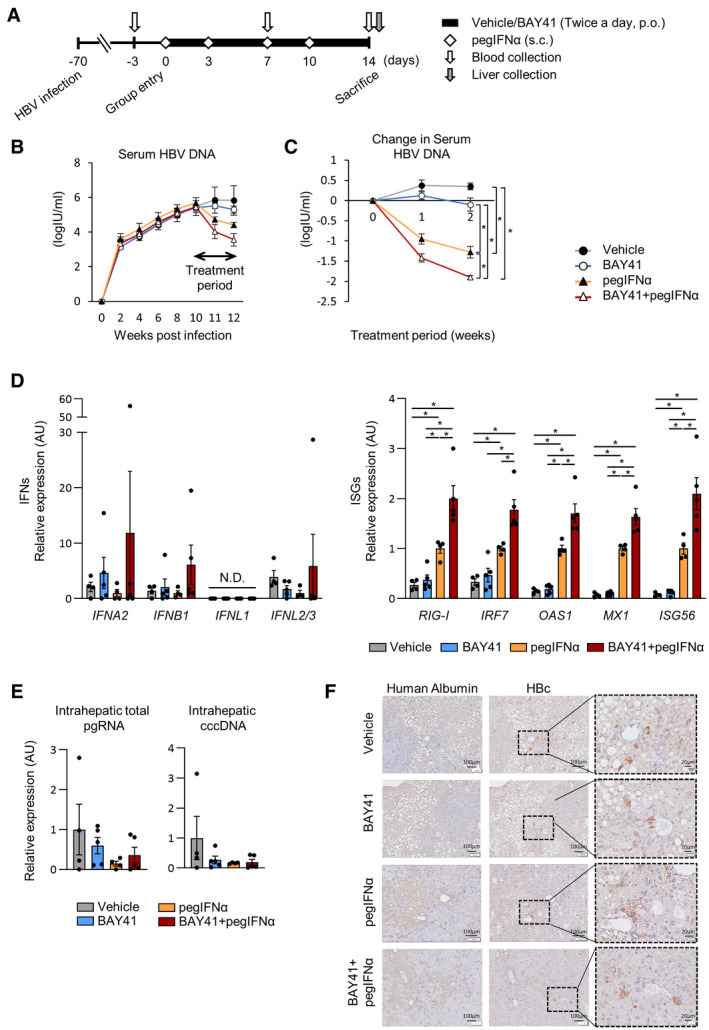
BAY41 enhances the intrahepatic ISG expression induced by pegIFN‐α in HBV‐infected human liver–chimeric mice, and BAY41 and pegIFN‐α combination therapy reduces serum HBV‐DNA levels more effectively than BAY41 or pegIFN‐α alone. HBV‐infected mice were treated with vehicle (n = 4), BAY41 (40 mg/kg, twice a day, p.o.) (n = 5), pegIFN‐α (25 mg/kg, twice per week, s.c.) (n = 4), or the combination of BAY41 and pegIFNα (n = 5) for 14 days. (A) Schematic of the experimental procedure. (B) Serum HBV‐DNA levels from inoculation to the end of the treatment. (C) Change in the serum HBV‐DNA levels over the treatment period. (D) Analysis of the intrahepatic mRNA expression levels of human‐specific IFN and ISGs. The results are presented as relative levels with the levels of each datapoint of mice treated with pegIFN‐α alone set to 1. Dot plot shows individual values. (E) Intrahepatic pgRNA and cccDNA levels at the end of the treatment. Dot plot shows individual values. (F) Representative image of HBc immunohistochemistry. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. Abbreviations: p.o., per os; s.c., subcutaneous administration.
