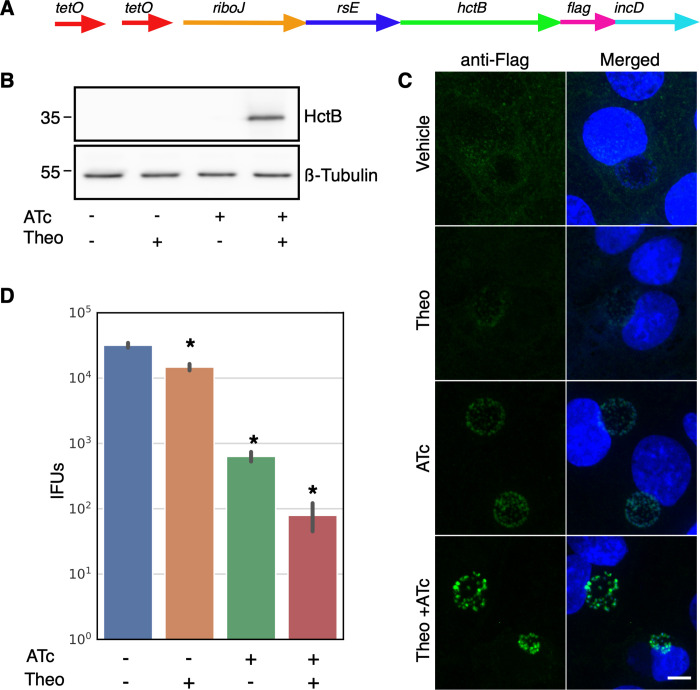
Fig 5. Characterization of p2TK2-SW2-Tet-J-E-hctB-flag.
A) Schematic of the Te-riboJ-E-hctB-flag construct. HctB expression is controlled by an aTc inducible promoter, riboJ insulator and the riboE riboswitch. B) Anti-flag western blot of Cos-7 cells infected with L2-Tet-J-E-hctB-flag comparing expression of theophylline treated and untreated cultures. Cells were induced with 0.5 mM theophylline, 30ng/ml aTc, both aTc and theophylline or vehicle only at 16 hpi and proteins were harvested at 30 hpi. HctB-flag expression was only detected in the samples induced with both aTc and theophylline. C) Confocal micrographs of Cos-7 cells infected with L2-Tet-riboJ-E-hctB-flag, induced with 0.5 mM theophylline, 30ng/ml aTc, both aTc and theophylline or vehicle only at 16 hpi and fixed and stained with DAPI (blue) for confocal microscopy at 30 hpi. The flag tag was stained with a primary antibody to the flag and an alexa 488 anti-mouse secondary antibody (green). Size bar = 10 μm. D) Production of infectious progeny was determined using a reinfection assay. Cos-7 cells were infected with L2-Tet-J-E-hctB-flag and the production of infectious progeny was determined at 48 hpi after induction with 0.5 mM theophylline, 30ng/ml aTc, both aTc and theophylline or vehicle only at 16 hpi. Asterisks denote p-values < 0.05. Error bars = SEM.