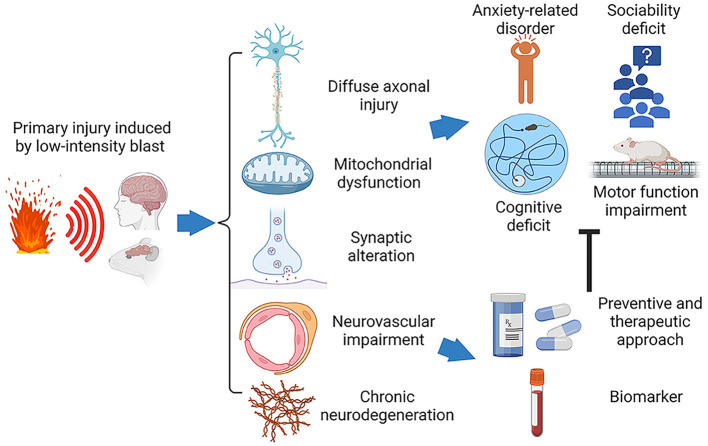
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the pathophysiology and behavioral impairments in LIB-induced mTBI. Traumatic brain injury induced by primary low-intensity blast (LIB) results in cellular and subcellular deficits, including diffuse axonal injury, mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic alteration, neurovascular impairment, and chronic neurodegeneration. These pathophysiological abnormalities lead to neurobehavioral dysfunctions, such as cognitive deficits, anxiety-related disorder, sociability deficit, and motor function impairment. The ongoing efforts targeting on these pathophysiological abnormalities to advance development of preventive and therapeutic solutions and specific biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment.