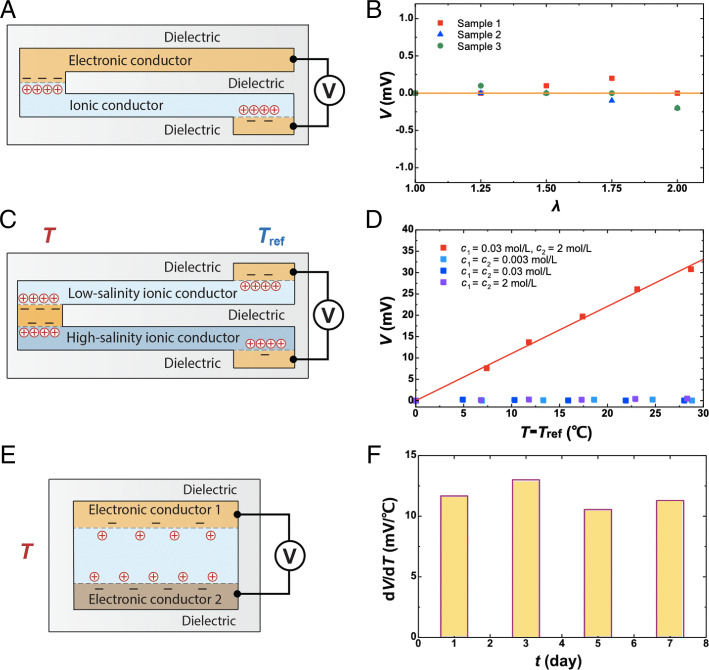
Fig. 3.
Ionotronic thermometry of several designs. (A) An electronic conductor and an ionic conductor are both elastomeric and stretchable. (B) At room temperature, stretch of the conductors negligibly affects voltage. A solid line is drawn to guide the eye. (C) The two ionic conductors have different ionic concentrations. (D) This difference causes a change in voltage when the temperature changes. The solid line is a linear fit to the data. (E) An ionic conductor is sandwiched between two dissimilar electronic conductors. The voltage between the two electronic conductors changes with temperature. (F) The sensitivity remains nearly constant over days.