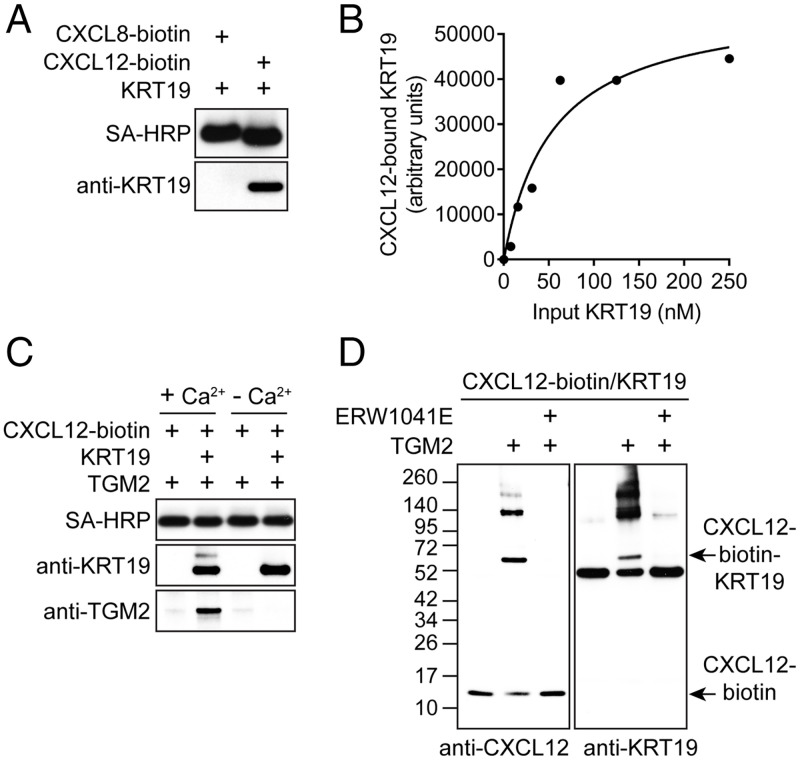
Fig. 2.
The interactions among CXCL12, KRT19, and TGM2. (A) Biotinylated human CXCL8 or CXCL12 was immobilized on SA beads, which were incubated with KRT19. The bead-bound proteins were eluted with SDS and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with SA-HRP or anti-KRT19 antibody. (B) SA beads bearing CXCL12–biotin were incubated with increasing concentrations of KRT19. Bound KRT19 was detected by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-KRT19 antibody, and intensities of the KRT19 bands were measured. (C) CXCL12–biotin that was immobilized on SA beads was incubated at 4 °C with TGM2 in the absence or presence of KRT19 and in the absence or presence of 10 mM CaCl2. The bound proteins were eluted and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with SA-HRP and antibodies to KRT19 and TGM2. (D) SA beads bearing preformed complexes of CXCL12–biotin and KRT19 were incubated at 20 °C for 15 min with TGM2 in the absence or presence of the TGM2 inhibitor ERW1041E. The proteins were eluted from the beads and detected by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies to CXCL12 and KRT19.