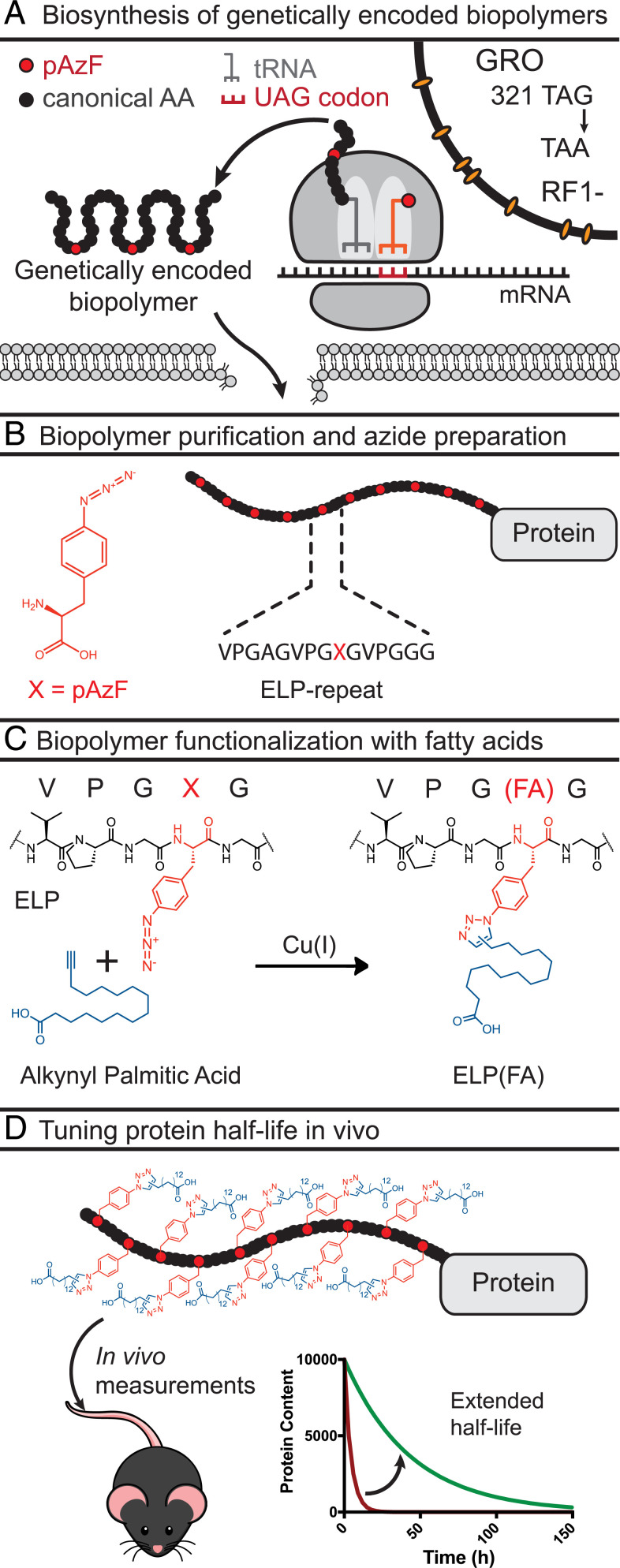
Fig. 1.
Biosynthesis and functionalization of genetically encoded biopolymers for half-life extension of proteins. (A) Site-specific multisite incorporation of pAzF at UAG codons in the GRO. All 321 TAG codons in E. coli were genomically recoded to TAA. To create the GRO, RF1 was deleted. The canonical amino acids and pAzF are shown as black and red circles, respectively. The TAG codon is converted into a sense codon for multisite incorporation of pAzF. (B) Schematic of the ELP-protein with 10 pAzF residues. The chemical structure of pAzF and the sequence of a single ELP repeat are shown. (C) Functionalization of azido groups in ELPs through copper(I)-mediated click chemistry with alkynyl palmitic acid. (D) Functionalized biopolymers are characterized in mice to study impact on half-life.