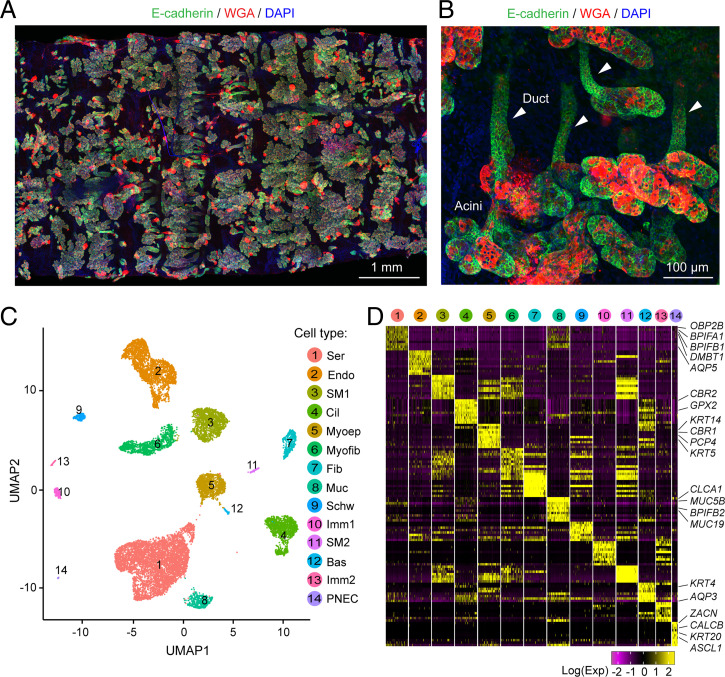
Fig. 1.
scRNA-seq of newborn pig SMGs reveals multiple cell types. (A) Representative immunofluorescent image of SMGs after tissue was removed from the cartilage. Images were taken from the basolateral side of the tissue and stitched together. Staining is E-cadherin (green, an epithelial marker), WGA (red, a lectin interacting with MUC5B), and DAPI (blue). Structures with E-cadherin and WGA double-positive signals are SMGs. (B) Representative image of individual SMGs stained with E-cadherin and WGA in whole-mount SMG tissues. Acini are at the bottom and ducts are indicated with arrowheads. (C) UMAP of 14 cell clusters in scRNA-seq of SMG and surrounding tissues. Bas; basal cells; Cil, ciliated cells; Endo, endothelial cells; Fib, fibroblasts; Imm, immune cells; Muc, mucous cells; Myoep, myoepithelial cells; Myofib, myofibroblasts; Schw, schwann cells; Ser, serous cells; SM, smooth muscle cells. (D) Heatmap of top 10 cell-type signature genes. Representative markers from epithelial clusters are shown. Colors indicated scaled single-cell gene expression (maximum 200 cells were shown) at natural log scale.