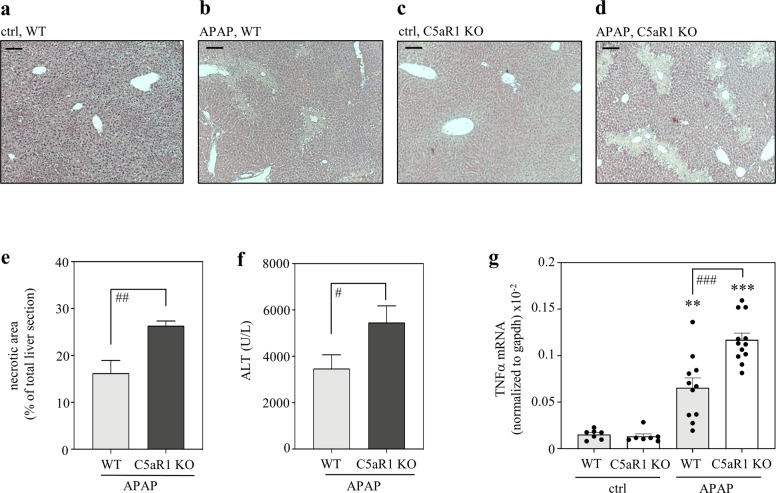
Fig. 4. C5aR1-deficient mice display aggravated APAP-induced ALI.
C57BL/6J C5aR1-deficient mice and their wild-type counterparts received 0.9% NaCl (control groups) or APAP (300 mg/kg). After 30 h, mice were sacrificed and liver tissue and sera were analyzed. a–d Representative liver sections (H&E staining) of vehicle-treated control (wild-type (n = 5), C5aR1-decicient (n = 5)) or APAP-treated (wild-type (n = 11), C5aR1-deficient (n = 12)) mice. e Analysis by BZ-II analyzer software of necrotic areas in H&E-stained liver sections from APAP-treated mice (wild-type, n = 11; c5ar1−/−, n = 12; ##p < 0.01). f Liver damage as detected by serum ALT (wild-type, n = 11; c5ar1−/−, n = 12; #p < 0.05). g Hepatic mRNA was isolated from 0.9% NaCl-treated control groups (each n = 7), from APAP-treated C5aR1-deficient mice (n = 12), and from their APAP-treated wild-type counterparts (n = 11). TNFα mRNA, determined by real-time PCR, was normalized to GAPDH and is shown as absolute values (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control of the respective genotype; ###p < 0.001). Statistical analysis on raw data: e, f Student’s t-test, data are shown as means ± s.e.m. g ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, data are shown as means ± s.e.m. Wild-type mice, WT; knockout mice, KO. Scale bars: 50 μm.