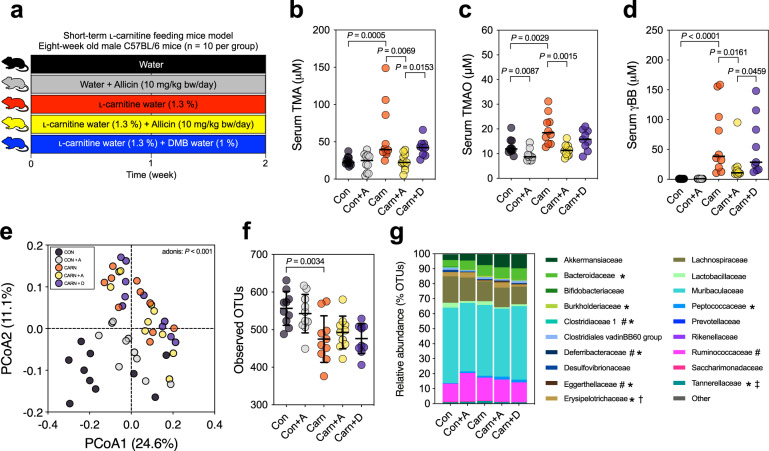
Fig. 1. Allicin reduced serum TMA, TMAO, and γBB levels, and ʟ-carnitine principally changed the fecal microbiome composition in ʟ-carnitine-fed male C57BL/6 J mice (n = 10 per group).
a Experimental design; b serum TMA; c serum TMAO; d serum γBB; e principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plot with Bray−Curtis dissimilarity; f observed OTUs α-diversity indices; and g relative abundance of fecal microbiota at family level. Dot plots are expressed as the mean ± SD or median; statistical analyses of serum bacterial metabolites were performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test Con vs. Con + A group, Con vs. Carn group; Kruskal–Wallis tests with Dunn’s multiple comparisons, Carn vs. Carn + A group, Carn vs. Carn + D group, and Carn + A vs. Carn + D group. Gut microbiota ɑ-diversity was determined using the unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s range test. The statistical analyses of the relative abundance were performed using the unpaired Wilcoxon signed-rank test with the false discovery rate (FDR), Con vs. Con + A group (#P < 0.1); Con vs. Carn group (*P < 0.1); Carn vs. Carn + A group (†P < 0.1); Carn + D group (‡P < 0.1).