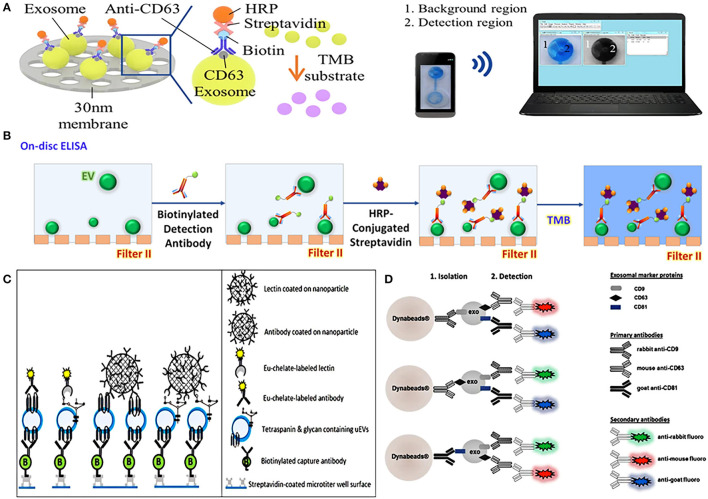
Figure 4.
Platforms based on nanomaterials for urinary EVs direct detection. (A) Schematic representation of urinary exosomes detection using on-chip ELISA with biotinylated anti-CD63 and streptavidin-HRP. Reprinted with permission from Liang et al. (71). (B) Schematic of a dual-function nanomaterials device (Exodisc) to detect urinary EVs through on-chip ELISA with biotinylated anti-CD9 and streptavidin-HRP. Reprinted with permission from Woo et al. (65). (C) Schematic of nanoparticles-based device combined Eu3+-doped nanoparticles with time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay (TRFIA) for detecting urinary EVs. Reprinted with permission from Islam et al. (83). (D) Schematic representation of nanoparticles complexes combined nanomagnetic beads, three specific antibodies of rabbit-anti CD9, mouse-anti CD63, and goat-anti CD81, and the corresponding secondary antibodies for detecting urinary EVs. Reprinted with permission from Hildonen et al. (75).