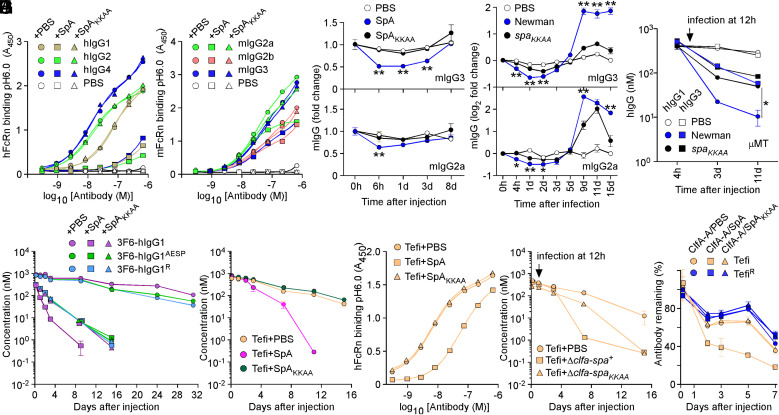
Fig. 4.
SpA influences the stability of antibodies in vivo. (A and B) Human and mouse hFcRn/mFcRn binding to human (A) and mouse (B) IgG at pH 6.0 was measured in the presence of PBS, SpA, or SpAKKAA by ELISA (n = 3 assays). ELISA plates were coated with hIgG, mIgG, or mock (PBS). Bound biotinylated FcRn was detected with HRP-conjugated streptavidin, and absorbances were recorded at 450 nm (A450). (C–D) Fold change over time of the serum concentration of mIgG2a and mIgG3 following injection of PBS, SpA, or SpAKKAA (C) and infection with mock (PBS), Newman, or its spaKKAA variant in BALB/c mice (D) (n = 4 animals per group). (E) hIgG1 and hIgG3 concentrations over time in μMT mice infected with mock (PBS), Newman, or spaKKAA 12 h after administration of hIgG1/3 (n = 4 mice per group). (F and G) Serum concentrations over time of test antibodies following injection of PBS, SpA, or SpAKKAA in BALB/c mice (n = 4 mice per group). (H) hFcRn binding to Tefi at pH 6.0 was measured in the presence of PBS, SpA, or SpAKKAA by ELISA (n = 3 assays). Bound FcRn was detected as in A. (I) Serum concentrations over time of test antibodies in BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per group). Animals were infected with the Newman variants Δclfa-spa+ or Δclfa-spaKKAA or PBS (mock) treated 12 h after the administration of test antibodies. (J) ICs of test antibodies Tefi/TefiR and cognate antigen ClfA-A were injected in BALB/c mice (n = 5 mice per group) along with PBS, SpA, or SpAKKAA, and the remaining fraction of test antibodies was measured over time. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and representative of at least two independent experiments (A, B, and H). Significant differences were identified by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttests (**P < 0.01; *P < 0.05).