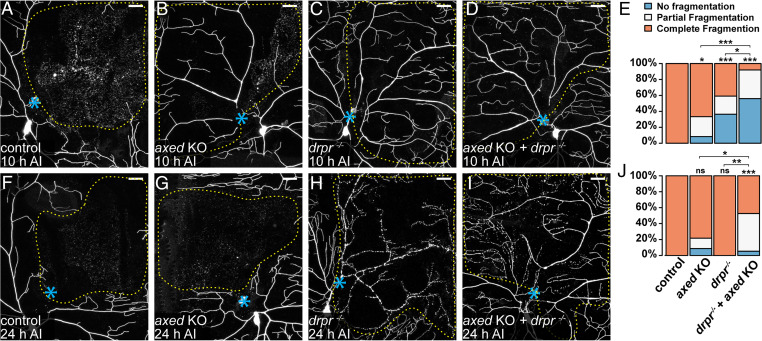
Fig. 6.
Axed promotes self-destruction of injured dendrites in parallel with Drpr-dependent phagocytosis. (A–D) Partial dendritic fields of wild-type (A), axed KO (B), drpr−/− (C), and axed KO + drpr−/− (D) ddaC neurons 10 h AI. B shows partial fragmentation; C and D show no fragmentation. (E) Quantification of dendrite fragmentation showing percentages of neurons undergoing no fragmentation, partial fragmentation, and complete fragmentation of injured dendrites at 10 h AI. n = number of neurons: wild-type (n = 18, nine animals); axed KO (n = 24, 10 animals); drpr−/− (n = 22, 11 animals); and axed KO + drpr−/− (n = 25, 11 animals) (Freeman–Halton extension of Fisher’s exact test). (F–I) Partial dendritic fields of wild-type (F), axed KO (G), drpr−/− (H), and axed KO + drpr−/− (I) ddaC neurons 24 h AI. I shows partial fragmentation. In all image panels, blue asterisks indicate injury sites; yellow dots outline regions covered by injured dendrites. Neurons were labeled by ppk > CD4-tdTom (A, B, F, and G) and ppk-CD4-tdTom (C, D, H, and I). Neuronal-specific KO was induced by SOP-Cas9 (B, D, G, and I). (Scale bars, 25 μm.) (J) Quantification of dendrite fragmentation showing percentages of neurons undergoing no fragmentation, partial fragmentation, and complete fragmentation of injured dendrites at 24 h AI. n = number of neurons: wild-type (n = 21, 12 animals); axed KO (n = 23, 10 animals); drpr−/− (n = 12, five animals); and axed KO + drpr−/− (n = 19, eight animals) (Freeman–Halton extension of Fisher’s exact test). For all quantifications, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, and ns, not significant. The significance level above each genotype is for comparison with the wild-type.