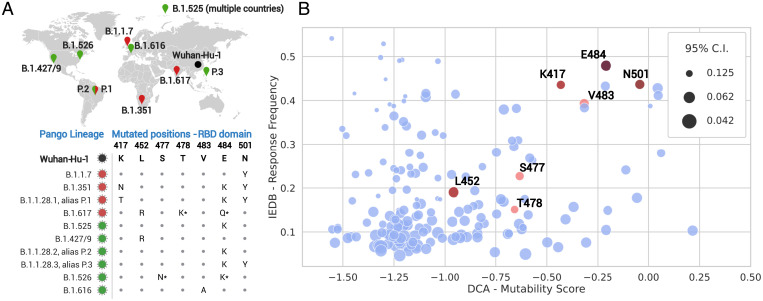
Fig. 3.
(A) SARS-CoV-2 strains classified in May 2021 as VOCs (red, now also named Alpha [B.1.1.7], Beta [B.1.351], Gamma [P.1], and Delta [B.1.617.2]) and VOIs (green). The figure shows the corresponding amino acid mutations with respect to the Wuhan-Hu-1 reference in the RBD domain and the geographical area where they were first detected. The B.1.617 lineage is divided into three sublineages; the E484Q and T478K (with asterisks) mutations are not shared by all sublineages. The same is true for E484K and S477N in the B.1.526 lineage. (B) The IEDB RF and the DCA mutability score for each position of the RBD domain. The upper right corner contains potentially dangerous positions, as they are predicted to be mutable (high DCA mutability score) and are shared by multiple positively responding epitopes (high IEDB RF). Mutated positions observed in VOCs and VOIs strains are depicted in red, and darker shades correspond to the most frequent mutations. The size of each point is inversely proportional to the IEDB 95% CI [size ∼1/(upper bound − lower bound)], thus larger points correspond to more statistically reliable IEDB RF.