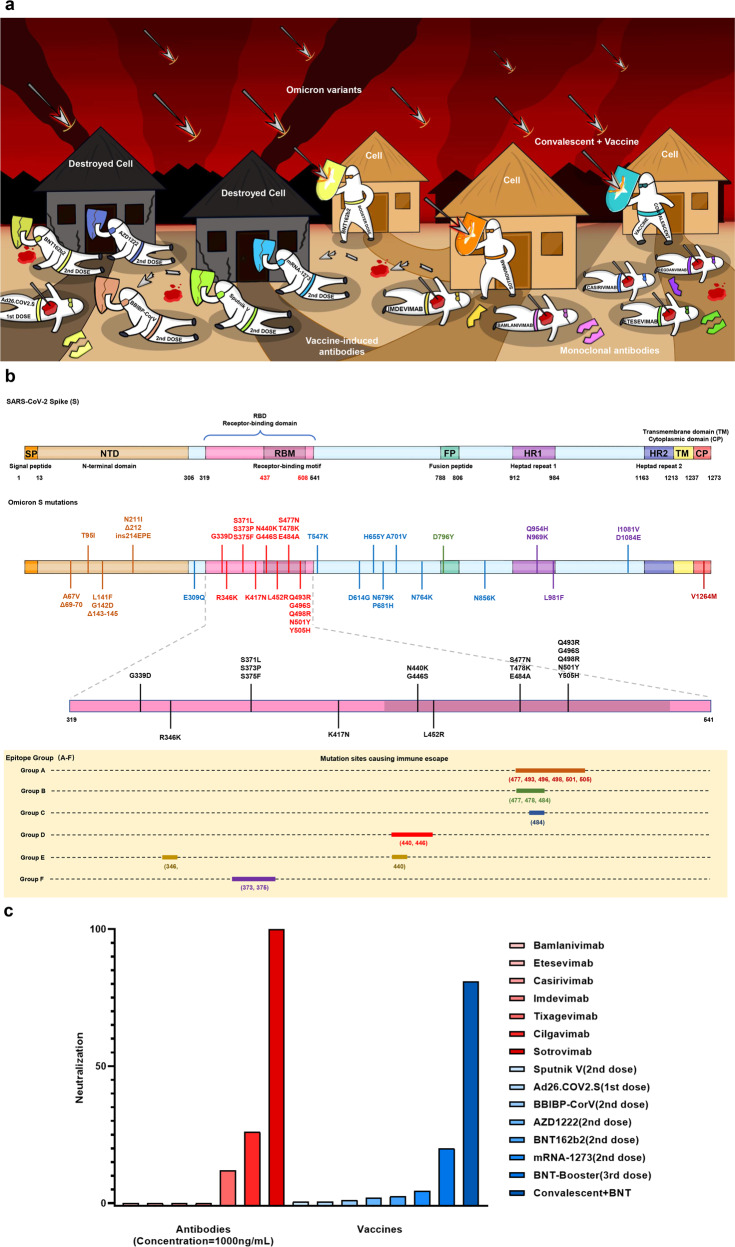
Fig. 1.
A schematic illustration of the variant Omicron escaping approved antibodies and vaccines. a FDA has approved several S protein-targeted monoclonal antibodies, in which Bamlanivimab, Etesevimab, Casirivimab, Imdevimab and CT-P59 (Regdanvimab) as well as the serum of all kinds of 2nd vaccine dose, fail to neutralize Omicron variant, while Sotrovimab and convalescent plus vaccinated plasma maintain the efficacy of Omicron variant. b Amino acid substitutions of Omicron variant in the spike protein, some of these mutations in RBD may affect the neutralization activity of group A–F antibodies, respectively. c The neutralizations of seven approved antibodies (Tixagevimab, Cilgavimab, Sotrovimab, Bamlanivimab, Etesevimab, Casirivimab, and Imdevimab) and six vaccines (BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, AZD1222, Sputnik V, BBIBP-CorV, Ad26.COV2.S) against Omicron are displayed, among which Bamlanivimab, Etesevimab, Casirivimab, and Imdevimab completely lose the neutralization while Sotrovimab still can neutralize Omicron variant effectively. All the 1st and 2nd dose vaccine serum fail to neutralize Omicron variant, and both the serum from convalescent patient with vaccination and booster dose of BNT162b2 retain neutralization activity against Omicron variant