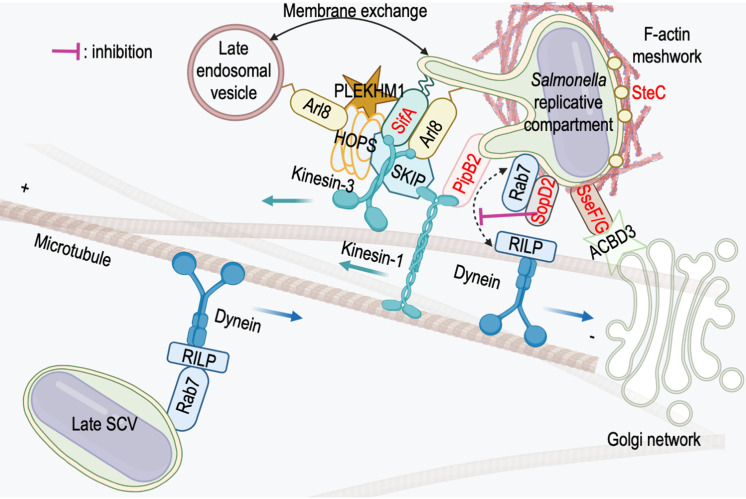
Figure 3. FIGURE 3: Salmonella effectors and host proteins interactions.
The small GTPase Rab7 is acquired during the maturation phase of the SCV and its presence is persistent thereafter. Its association with RILP allows the recruitment of dynein and the retrograde movement of the maturing Late SCV to the juxtanuclear region. Specific T3SS-2 effectors (in red) are localized on the replicative compartment. The presence of SopD2 maintains Rab7 in a GDP-bound form that does not bind RILP and prevents dynein recruitment. SteC has a kinase activity necessary for actin polymerization in the vicinity of SCVs/SITs. SseF/G anchor the SCV to the Golgi network via an interaction with the Golgi resident protein ACBD3. Both PipB2 and SifA recruit kinesin-1, respectively through a direct interaction or via SKIP. Kinesin-3 is recruited through its interaction with SifA and SKIP. SifA recruits the small GTPase Arl8 and these proteins are bound to the membrane by geranylgeranylation or acetylation, respectively. SKIP and PLEKHM1 compete to bind to SifA and Arl8 and both recruit the HOPS tethering complex on SCVs/SITs to initiate the fusion process with the late membrane compartments of the host cell.