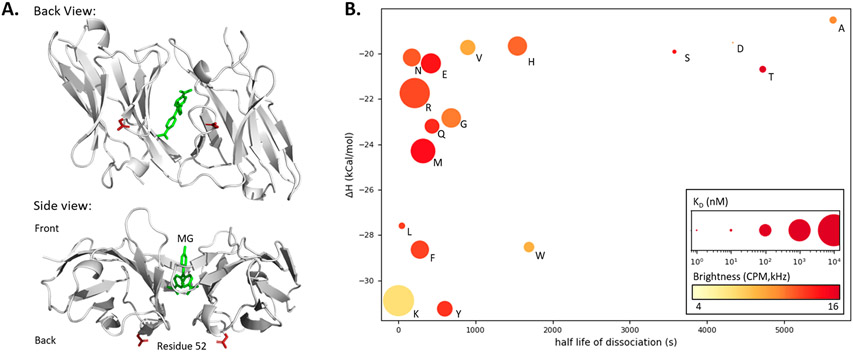
Figure 2.
Site-directed saturation mutagenesis to identify low-affinity L5 FAP mutants. (A) Crystal structure (PDB: 4K3H) of two L5* monomers binding Malachite Green (green) with top and side views. Residue 52 (red, E52D) is highlighted showing how direct participation in the MG binding pocket is unlikely since the residue is distal to the binding pocket and opposite the expected entry point of the dye. (B) Properties of monomeric L5*(E52X) variants: Isothermal calorimetry gave enthalpy values via titration of 4 μM protein with MG-2p. Rates were determined directly via fluorescence measurement (dissociation N = 4, association at four concentrations between 100 and 300 nM with N = 4). E, K dissociation rates were determined using equation kon = koff/KD. The KD was calculated based on fluorescence equilibrium titration (at 5 nM concentration of the L5 monomer protein) and is depicted as the size of the plotted point (nM, log scaling). Molecular brightness was measured by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and is depicted as a color gradient (red is brighter; Supporting Information Table 3).