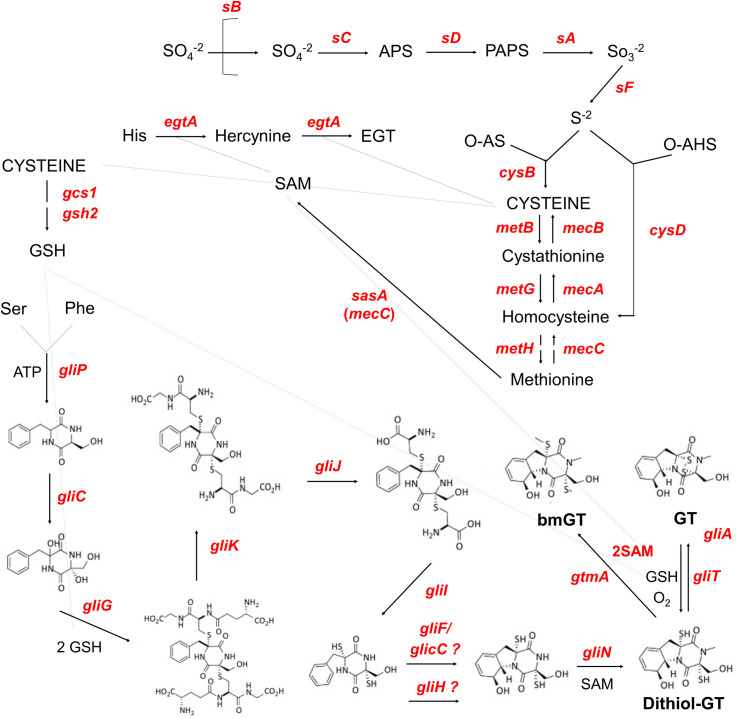
Fig 10. Schematic representation of the pathways that are important for GT production and self-defense.
– The pathways of sulfate assimilation, transsulfuration, and GT production are shown in the scheme. The depicted genes are: sB, sulfate transporter; sC, ATP sulfurylase; sD, adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate (APS) kinase; sA, 3’-phosphoadenosine-5’-phosphosulfate (PAPS) reductase; sF, β-subunit of the sulfite reductase; AFUA_6G08920, α-subunit of the sulfite reductase; cysB, cysteine synthase; metB, cystathione-ϒ-synthase; metG, cysthationine-β-lyase; metH, methionine synthase; mecC, 5-adenosylmethionine synthetase; mecA, cystathionine-β-synthase; mecB, cystathionine- ϒ-lyase; cysD, homocysteine synthase; gliP, non-ribosomal peptide synthetase; gliC, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; gliG, glutathione-S-transferase; gliK, unknown protein; gliJ, membrane dipeptidase; gliI, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase; gliF, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; gliC, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase; gliH, acetyl transferase; gliN, methyltransferase; gliT, gliotoxin sulfhydryl oxidase; gliA, major facilitator type glioxin transporter; gcs1, glutamate cysteine-ligase; gsh2, glutathione synthase; egtA, ergothioneine synthase; and gtmA, bis-thiomethyltransferase. Abbreviations: O-AS, O-acetylserine; O-HS, O-acetylhomoserine; GSH, glutathione; SAM, S-adenosyl methionine; EGT, ergothioneine; bmGT, bisdethiobis(methylthio)-gliotoxin; and GT, gliotoxin.