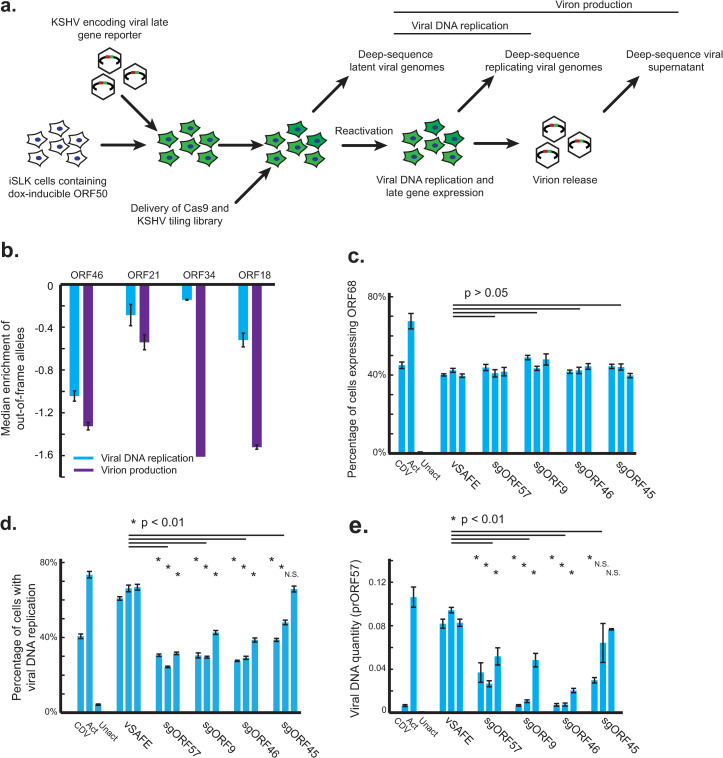
Fig 3. Deep viral sequencing identifies ORF46 requirement for viral DNA replication.
a) Design of targeted deep-sequencing experiment. Four viral loci were amplified and deep-sequenced: ORF21, ORF18, ORF34, and ORF46. b) Median enrichment across the coding region of the gene of out-of-frame indels in replicating cells relative to latent cells (Viral DNA replication) or the supernatant relative to latent cells (Virion production). Error bars are standard error from two replicates. One replicate of ORF34 supernatant sample was excluded due to uneven coverage. c,d,e) Three individual sgRNAs were lentivirally delivered to KSHV-infected iSLK cells targeting the indicated viral ORF. Error bars are standard error from four independent reactivations. CDV-treated, reactivated, and unactivated parental cells are included as controls, along with three vSAFE sgRNAs targeting an ORF-free region of the BAC. P values were calculated using a single-tailed, equal variance Student’s t-test, with the least significant value used when compared to each individual vSAFE sgRNA. NS indicates non-significance (P>0.01). c) Reactivation and early gene expression was measured using a KSHV virus containing a HaloTag fusion to a viral early gene, ORF68. d) Measuring viral DNA replication by percentage positive EdU staining. A 2-hour pulse of EdU was delivered 48 hours post reactivation. Cells were then fixed, and click chemistry was used to measure EdU incorporation by flow cytometry. Unreactivated cells were used to establish gates for flow cytometry, where subgenomic EdU incorporation was measured as viral DNA replication. e) DNA was extracted 48 hours post reactivation, and qPCR of the viral promoter of ORF57 was used to measure the amount of viral DNA.