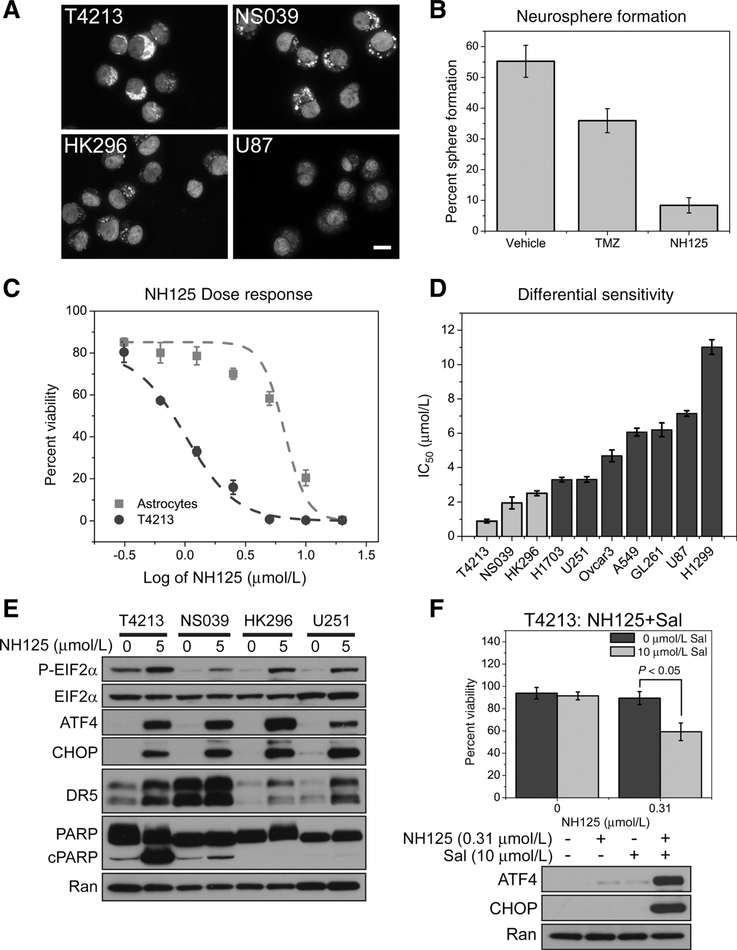
Figure 3.
GSC that enrich for CD133 experience a reduction in viability following NH125-mediated ISR signaling. A, Representative immunofluorescence images of untreated GSCs taken under 63× magnification (scale bar = 15 μm). Images are presented as an overlay of CD133 (cytoplasmic staining) and DAPI (nuclear staining), showing that each stem cell line has varying degrees of CD133 expression when compared with U87. B, Assaying for sphere formation following a 7-day treatment with either vehicle, TMZ or NH125 reveals a decrease in neurospheres following NH125 treatment. Means and SDs are calculated from biological triplicates. C, An identical NH125 dilution series is applied to both NHAs and T4213 GSC, revealing a six-fold decrease in the IC50 for T4213. Data points represent means and SDs of normalized viability calculated from biological triplicates. D, IC50 values from a panel of NH125-treated cell lines highlight GSC (light gray) sensitivity to NH125. Means and SDs are calculated from three independent experiments. E, GSC and U251 were incubated with either 0 μmol/L NH125 (0.1% DMSO) or 5 μmol/L NH125 for 24 hours. Lysate was then probed for ATF4, CHOP, DR5, and PARP cleavage. All cell lines demonstrate an increase in ATF4, CHOP, and DR5 expression. PARP cleavage is observed in NH125- treated T4213 and NS039 at the time and concentration tested. F, DMSO and NH125 T4213 were co-incubated with 10 μmol/L Salubrinal (Sal) for 24 hours. Means and SDs are calculated from three independent experiments revealing a decrease in viability following the addition of Sal (P < 0.05). Only combination treatment of T4213 with NH125 and Sal produces an increase in ATF4 and CHOP expression.