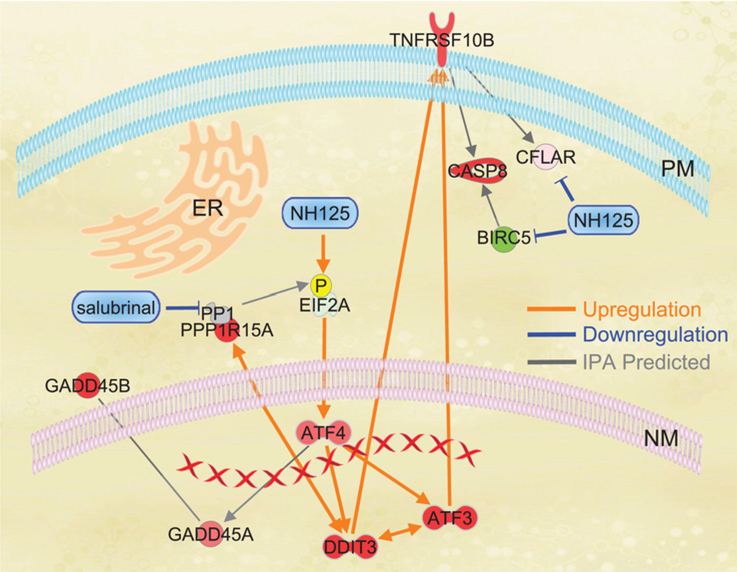
Figure 7.
Overlay of IPA expression data and integrated stress signaling events in NH125-treated GSC. Red and green shading are reflective of increased or decreased expression respectively as predicted by IPA. Orange lines are experimentally observed interactions that lead to an increase in expression. Blue lines are experimentally validated interactions that lead to a decrease in expression or degradation/inhibition of a signaling molecule. Gray lines are interactions predicted by IPA algorithms. Experimental data demonstrate that incubation with NH125 leads to phosphorylation of EIF2α, increased translation of ATF4, expression of DDIT3 (CHOP), and ATF3. Interconnection of ATF3 and DDIT3 was predicted by IPA with both signaling events contributing to an increase in TNFRSF10B (DR5) expression. Translation of ATF4 was found to be indirectly linked to increased expression of GADD45A and GADD45B through IPA. NH125 leads a decrease in BIRC5 (Survivin) and CLFAR (C-FLIP) protein. BIRC5 (Survivin) interacts with CASP8 (Caspase 8), and CLFAR (C-FLIP) interacts directly with TNFRSF10B. Whole transcriptome analysis and co-incubation studies with Salubrinal provide evidence that expression of DDIT3 and PPP1R15A (GADD34)/PP1 are interconnected. Co-incubation with Salubrinal inhibits PPP1R15A blocking de-phosphorylation of EIF2α.