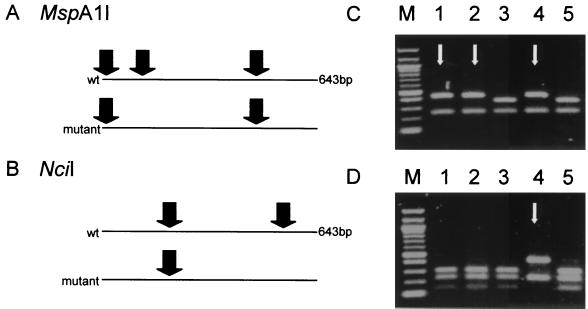
FIG. 1.
(A and B) REA of a 643-bp amplicon of M. tuberculosis katG. (A) In order to detect a mutation at codon 315, the amplicon was digested by MspA1I. A wild-type (wt) amplicon was cut at three positions, but an amplicon with a mutation in the recognition sequence encompassing codon 315 was cut at only two. (B) NciI was used to detect the mutation at codon 463. NciI cut a wild-type amplicon at two positions, but an amplicon with a mutation in the recognition sequence containing codon 463 was cut at only one. (C and D) Gel electrophoresis of digested fragments derived from five different isolates (1 to 5) of M. tuberculosis allows discrimination of wild-type and mutant isolates for codons 315 (C) and 463 (D). Arrows indicate mutant DNA fragments. Lane M, 100-bp ladder with bands at 0.1-kb intervals, starting at 0.1 kb.