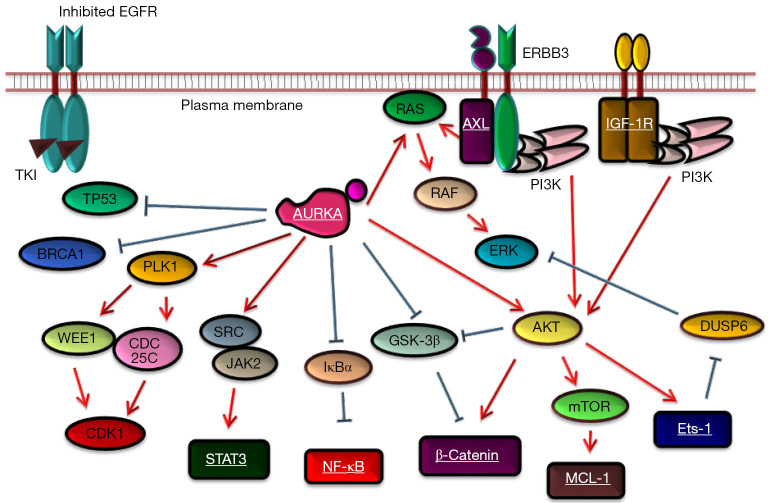
Figure 1.
Scheme of the AURKA pathway and molecules that are reported to cause the drug-tolerant state [AXL (20), IGF-1R (7,21), NF-κB (8,9,13,14,17), β-catenin (10), STAT3 (11,12), Ets-1 (15), and MCL-1 (18), which are highlighted in white bold letters] in lung cancer cells carrying EGFR mutations upon EGFR-TKI treatment. It is interesting that the compound screening by Shah and colleagues also identified that compounds with the 3rd to 7th highest synergy scores were inhibitors of PI3K, AKT, mTOR, or Src (although they are not highlighted, they may have some roles in the drug-tolerant state; as a side note, the compounds with the highest two synergy scores were AURK inhibitors) (23). Some other candidate factors that might be related to drug tolerance; e.g., altered chromatin state (7), ER stress signaling (19), or glucose metabolism (16), are not illustrated in this figure; however, it is noteworthy that AURKA inhibition will lead to the inhibition of multiple potential causes of drug tolerance. The figure was generated using a combination of results from multiple published works related to the AURKA pathway (26-29) or drug tolerance states (15,18,20,23); therefore, it is possible that it may overestimate the roles of AURKA. AURKA, aurora kinase A; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.