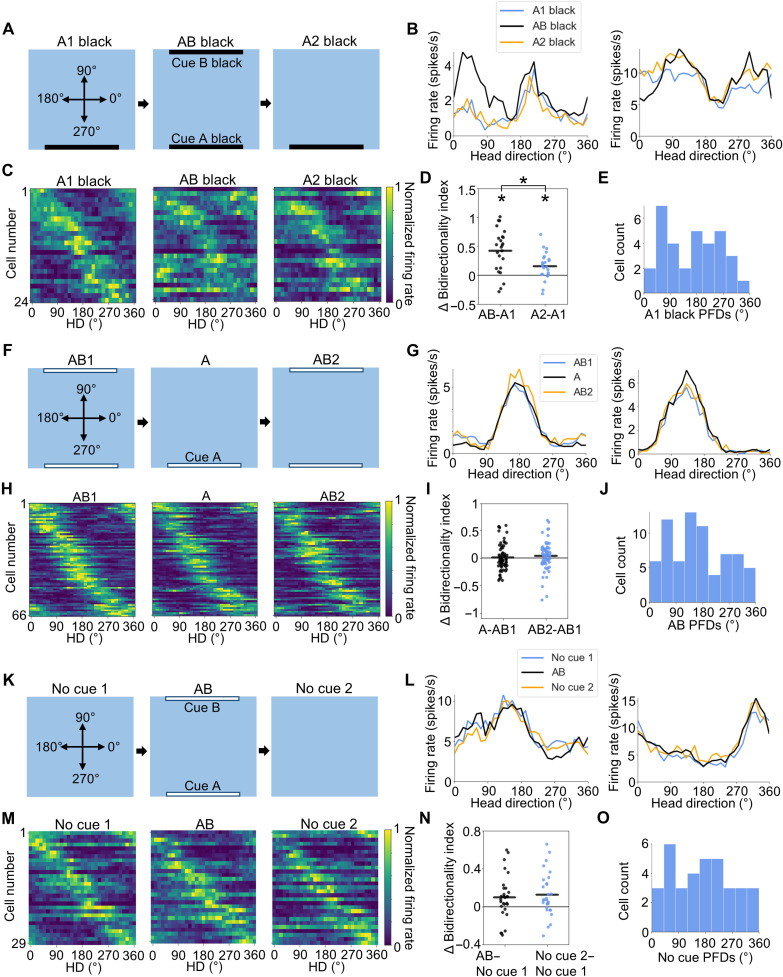
Fig. 6. Effects of habituation to different cue configurations.
(A) Experimental design for the AB black experiment. Top-down view showing the locations of visual cues across A1 black, AB black, and A2 black sessions. (B) Tuning curves for two example POR LM-HD cells from the AB black experiment that showed bidirectional tuning in the AB black session. (C) Normalized tuning curves for all POR LM-HD cells recorded in the AB black experiment. (D) Comparison of BI between A1 black and both AB black and A2 black sessions. Asterisk (*) denotes statistical significance. Note that bidirectionality was increased in the AB black session relative to both A1 black and A2 black sessions, although it was slightly elevated in the A2 black session. (E) Distribution of HD PFDs for all LM-HD cells recorded in the A1 black session. (F) Experimental design for the AB1-A-AB2 experiment. (G) Tuning curves for two example POR LM-HD cells recorded across the sessions of the AB1-A-AB2 experiment that showed largely unidirectional tuning in all sessions. (H) Normalized tuning curves for all POR LM-HD cells recorded in the AB1-A-AB2 experiment. (I) Comparison of BI between AB1 and both A and AB2 sessions. (J) Distribution of HD PFDs for all LM-HD cells recorded in the AB1 session. (K) Experimental design for the No cue 1–AB–No cue 2 experiment. (L) Tuning curves for two example POR LM-HD cells recorded across the sessions of the No cue 1–AB–No cue 2 experiment that showed unidirectional tuning in all sessions. (M) Normalized tuning curves for all POR LM-HD cells recorded in the No cue 1–AB–No cue 2 experiment. (N) Comparison of BI between No cue 1 and both AB and No cue 2 sessions. (O) Distribution of HD PFDs for all LM-HD cells recorded in the No cue 1 session.