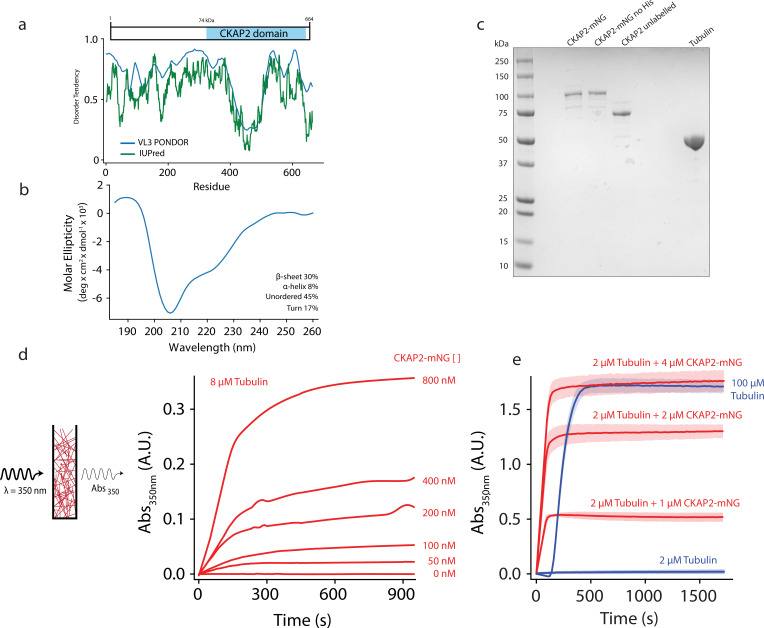
Figure 1. Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein 2 (CKAP2) is an intrinsically disordered protein that increases microtubule formation.
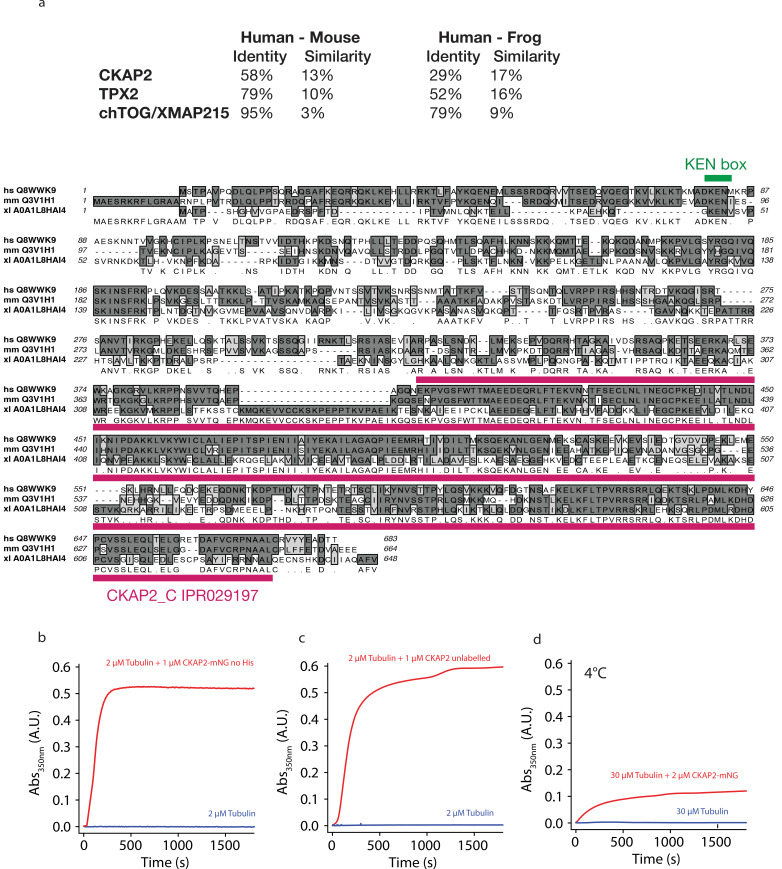
(a) Schematic of mmCKAP2 protein domains and disorder prediction (Dosztányi et al., 2005; Obradovic et al., 2003). (b) Circular dichroism of 4.5 μM CKAP2. (c) Coomassie Blue-stained sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) gel of 1 μg of purified recombinant CKAP2 constructs and 5 μg of purified tubulin. (d) Light scattering assay (turbidity) schematic and data following microtubule formation as apparent absorbance (Abs) over time for 8 µM tubulin with increasing concentrations of CKAP2-mNeonGreen (CKAP2-mNG) (n = 1). (e) Turbidity data for tubulin alone (blue) and addition of CKAP2-mNG (n = 3, mean ± standard deviation [SD]).