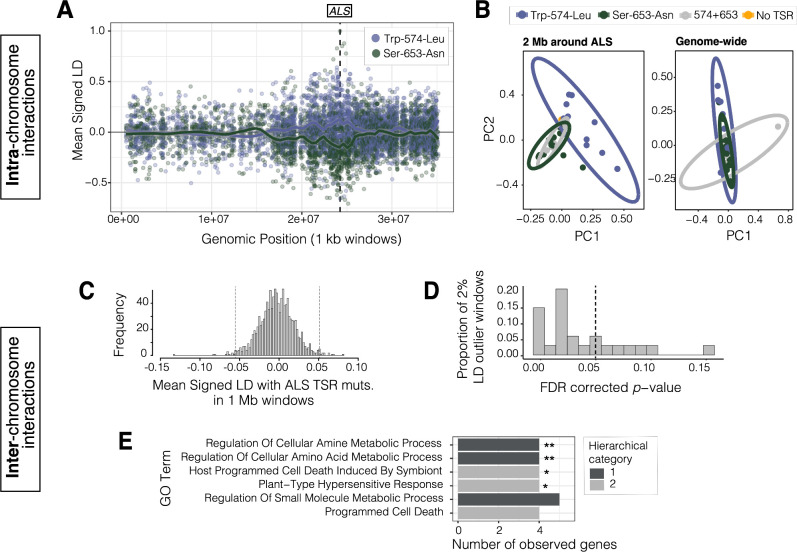
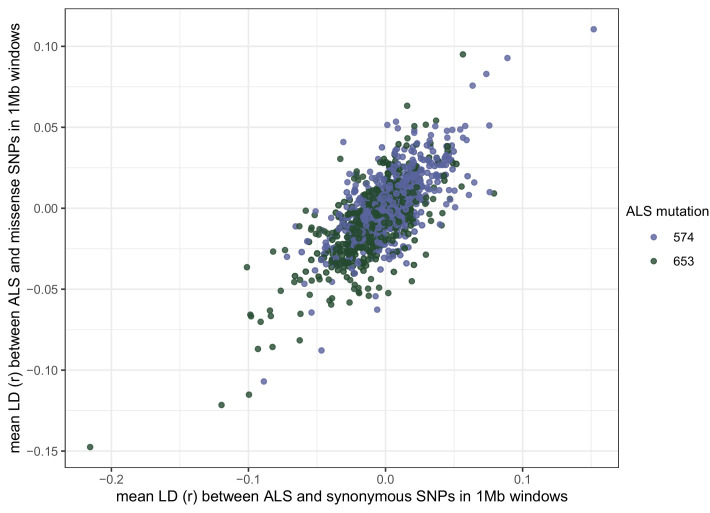
Figure 4. Signals of intra- and inter-chromosomal allelic interactions with target-site resistance mutations.
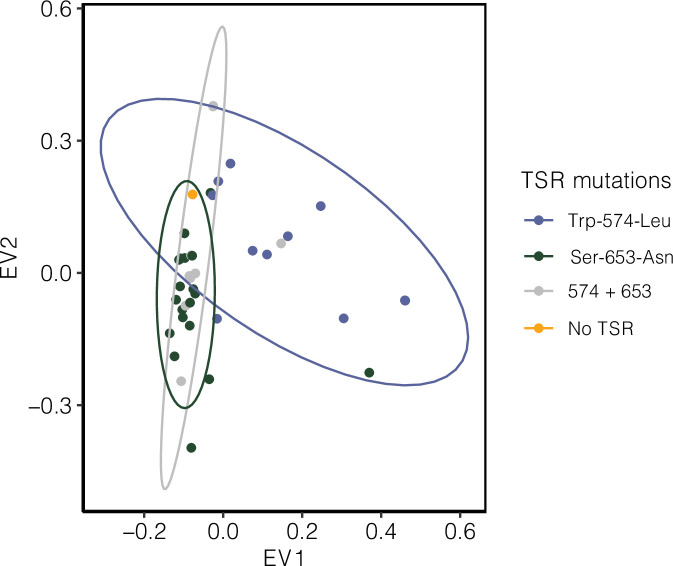
(A) The breadth of haplotype competition between TSR mutations, illustrated by repulsion linkage disequilibrium (opposite signed LD, r) between two target-site-resistance mutations and bi-allelic missense SNPs surrounding them on Scaffold 11 in Essex. Each point shows mean LD in non-overlapping 10 kb windows. A smoothing spline shows that missense SNPs tend to be in positive LD with ALS Trp-574-Leu but negative LD with ALS Ser-653-Asn in Essex. (B) Signatures of population structure for 2 Mb around ALS compared to genome-wide, based on PCAs of genotypes in Essex. Ellipses represent 95% CIs assuming a multivariate distribution. (C) Distribution of mean signed LD of ALS TSR resistance mutations (ALS 574 or 653) with 1 Mb windows genome-wide in Essex, excluding the ALS containing Scaffold 11. Upper and lower 1% quantile indicated by dashed vertical lines. (D) Distribution of p-values from top 2% of genome-wide windows with high absolute signed LD with ALS TSR mutations, from permuting individual assignment within genomic windows and recalculating LD 1,000 times. (E) GO terms significantly enriched for biological process after FDR correction from the set of 348 genes mapping to the top 13, 1 Mb windows that show significantly extreme LD with ALS TSR mutations in Essex. Number of asterisks represent significance level after bonferroni correction (** = p < 0.01, * = p < 0.05).