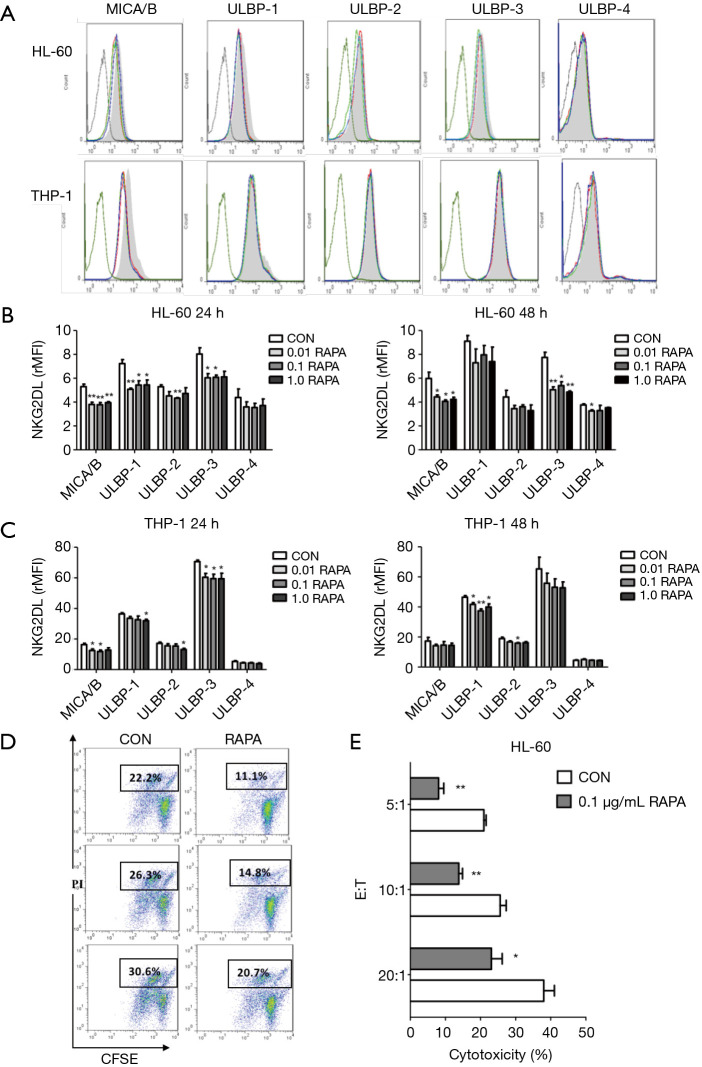
Figure 2.
RAPA downregulates the cytotoxic sensitivity of AML to NK cells by decreasing NKG2DL expression on AML cells. (A) Flow cytometry results of the expression of 5 NKG2D ligands expressed on both AML cells (HL-60 and THP-1) after various concentrations of RAPA (0, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0 µg/mL) treatment for 24 h. Black line, IgG; grey line, Con; red line, 0.01 µg/mL; green line, 0.1 µg/mL; blue line, 1.0 µg/mL; (B,C) the downregulation of rMFI levels of 5 NKG2D ligands (MICA/B, ULBP1-4) in HL-60 cells and THP-1 cells after RAPA treatment; (D) flow cytometry of cytotoxic sensitivity of HL-60 cells to NK cells. After RAPA treatment for 24 h, the cytotoxic sensitivity of HL-60 cells to NK cells significantly declined; (E) RAPA downregulated the cytotoxic sensitivity of HL-60 cells to NK cells at different E:T ratios. HL-60 cells were previously incubated with 0.1 µg/mL RAPA for 24 h and then co-cultured at a different effector-target ratio (E:T ratio). Results are reported as mean ± SD of the 3 independent experiments (B,C,E). *, P<0.05 vs. control group; **, P<0.01 vs. control group. RAPA, rapamycin; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; NK, natural killer; IgG, immunoglobulin G; rMFI, relative mean fluorescence intensity; SD, standard deviation.