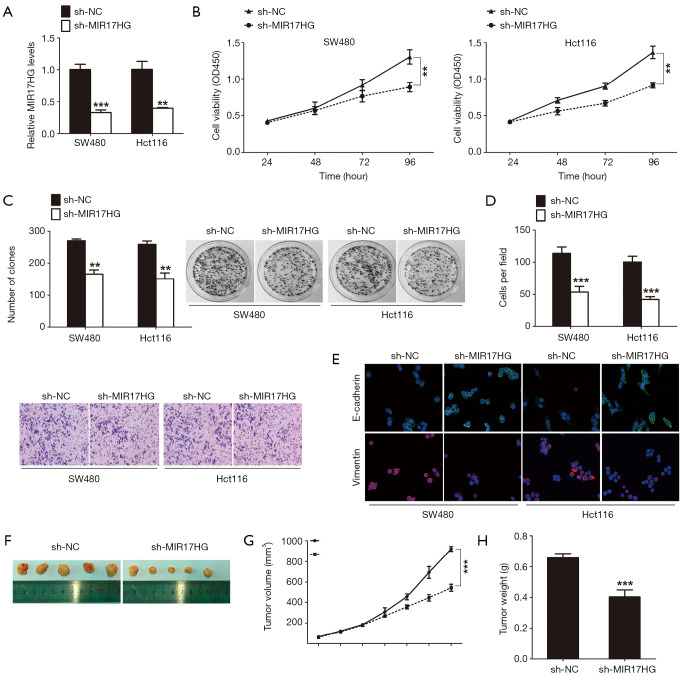
Figure 2.
Suppression of MIR17HG inhibits the progression of colon cancer in vitro and in vivo. (A) Relative levels of MIR17HG in colon cancer cells after treatment with sh-MRI17HG or sh-NC. (B) CCK-8 assay was carried out to detect the viability of transfected colon cancer cells. (C) Plate colony formation assay was performed to examine the proliferation of transfected colon cancer cells. (D) Transwell assay was performed to determine the invasive ability of transfected colon cancer cells (×200). (E) Confocal immunofluorescent assay demonstrated that downregulation of MIR17HG increased the expression of epithelial marker E-cadherin with a simultaneous decrease in the expression of mesenchymal marker Vimentin (×400). (F,G,H) In vivo tumor xenografts experiment showed that sh-MIR17HG transfected SW480 cells developed significantly smaller tumors than normal control group. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.