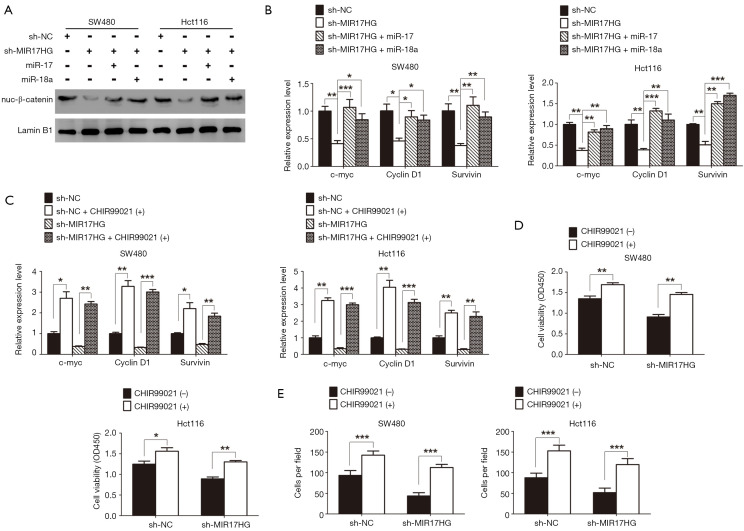
Figure 5.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is responsible for the oncogenic role of MIR17HG-miR-17/miR-18a axis in colon cancer. (A,B) Depletion of MIR17HG in colon cancer cells caused the suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, whereas miR-17 or miR-18a overexpression abrogated this effect. (C) The downstream target genes of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in sh-NC/sh-MIR17HG colon cancer cells were detected by qRT-PCR after treated with 10 µmol/L CHIR99021 for 36 hours. (D,E) Depletion of MIR17HG decreased the proliferative and invasive abilities of colon cancer cells, and these effects were rescued by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.