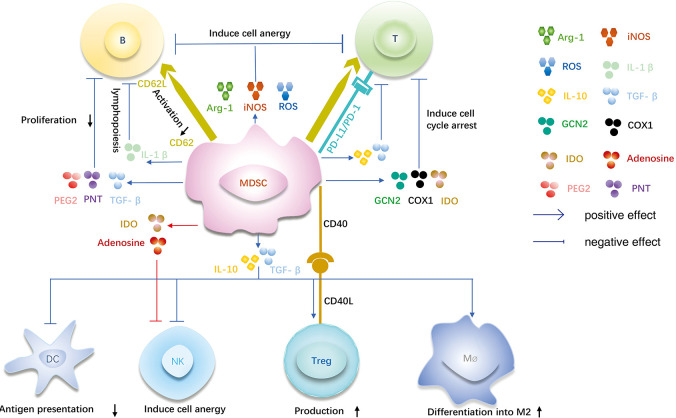
Figure 1.
Function of MDSCs. T cell: MDSCs can promote immune suppression by increasing the activity of arginase (Arg-1), iNOS and ROS; high expression of PD-L1 on MDSCs interacts with PD-1 on T cells; MDSCs can downregulate L-selectin (CD62L) and influence T cell function; Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase, COX1 and general control nonderepressible 2 will result in immune suppression; Transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-10 can produce direct immunosuppressive effect on T cells. B cell: MDSCs inhibit B cell proliferation and function by Arg-1, iNOS, ROS, PNT, PEG2 and TGF-β; the secretion of interleukin 1β inhibits B lymphopoiesis; MDSCs can down-regulates CD62L and influence B cell lymphopoiesis. DCs: TGF-β and IL-10 inhibit DC the function of antigen presentation. NK: TGF-β, IL-10, IDO and adenosine induce NK anergy. Tregs: the expression of CD40 on MDSCs induce Tregs accumulation; TGF-β and IL-10 increase the production. M ø: TGF-β and IL-10 exacerbate macrophage polarize towards to the M2 phenotype. MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PNT, peroxynitrite; DCs, dendritic cell; NK, natural killer cell; Tregs, regulatory cells; M ø, macrophage.