Figure 2.
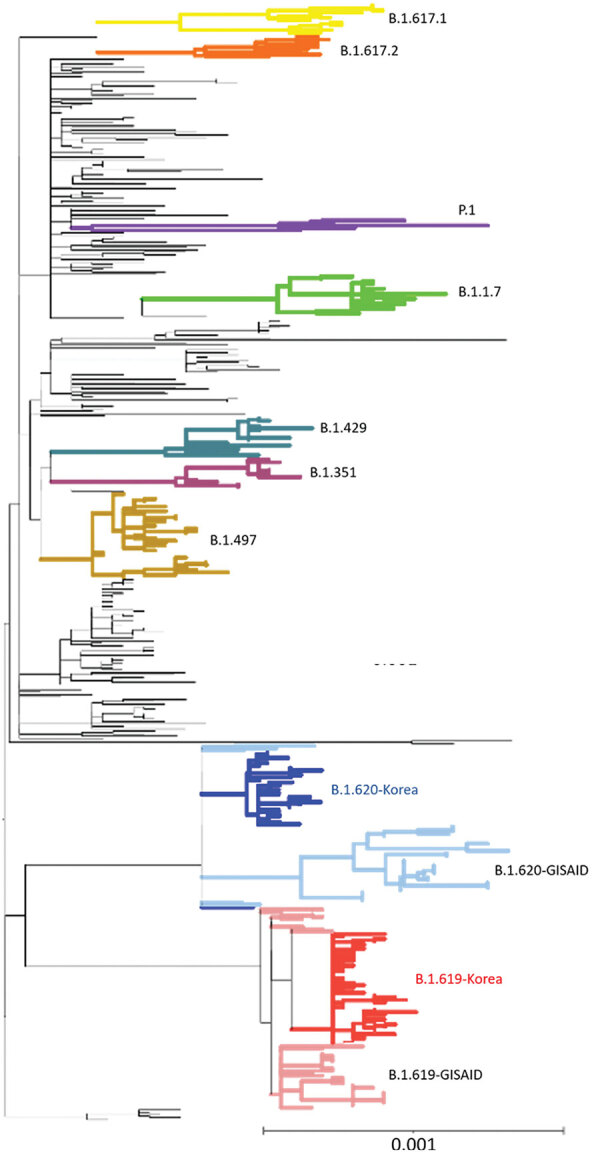
Phylogenetic analysis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 sequences, South Korea. A total of 457 sequences were used to construct the tree, including 37 sequences of B.1.619 lineage and 36 sequences of B.1.620 lineage from GISAID (https://www.gisaid.org). Each sequence was aligned to the reference sequence (Wuhan-Hu-1, GenBank accession no. NC_045512) using Geneious Prime software (https://www.geneious.com) and then manually trimmed to equal lengths. A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using FastTree version 2.1.9 (http://www.microbesonline.org/fasttree), under the general time reversible plus gamma nucleotide substitution model; the phylogenetic tree was visualized using iTOL (https://itol.embl.de). Four variants of concern (B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1, and B.1.617.2), 2 variants of interest (B.1.429 and B.1.617.1), and B.1.497, which were the major lineages of the GH clade in South Korea, are shown. Red indicates South Korea B.1.619 sequences and blue, B.1.620; pink indicates Europe B.1.619 sequences and light blue, B.1.620. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
