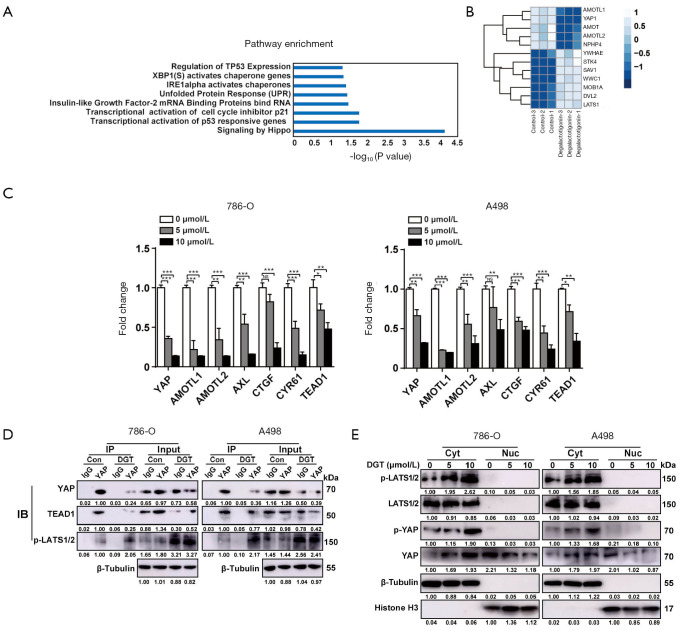
Figure 3.
Degalactotigonin inactivated yes-associated protein (YAP) signaling through facilitating large tumor suppressor 1/2 (LATS1/2) activation and YAP retention in the cytoplasm of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. (A) RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was carried out in 786-O cells treated with or without degalactotigonin. Signaling pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes in degalactotigonin-treated 786-O cells relative to untreated 786-O cells. (B) A heatmap depicting the significantly differentially expressed genes between the two groups is shown. (C) The mRNA expression levels of YAP, angiomotin-like protein 1 (AMOTL1), angiomotin-like protein 2 (AMOTL2), AXL receptor tyrosine kinase (AXL), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), cysteine-rich protein 61 (CYR61) and TEA domain transcription factor 1 (TEAD1) in untreated and degalactotigonin-treated clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells were examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). (D) Western blotting was performed to detect the results of coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) experiments to precipitate endogenous YAP with TEA domain transcription factor 1 (TEAD1) and phosphorylated large tumor suppressor 1/2 (p-LATS1/2) from untreated and degalactotigonin-treated 786-O and A498 cells. (E) Western blot analysis was used to detect phosphorylated large tumor suppressor 1/2 (p-LATS1/2), large tumor suppressor 1/2 (LATS1/2), phosphorylated yes-associated protein (p-YAP) and YAP in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of untreated and degalactotigonin-treated 786-O and A498 cells. β-Tubulin and Histone H3 served as internal controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. All P values are defined as follows: *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01 and ***, P<0.001.