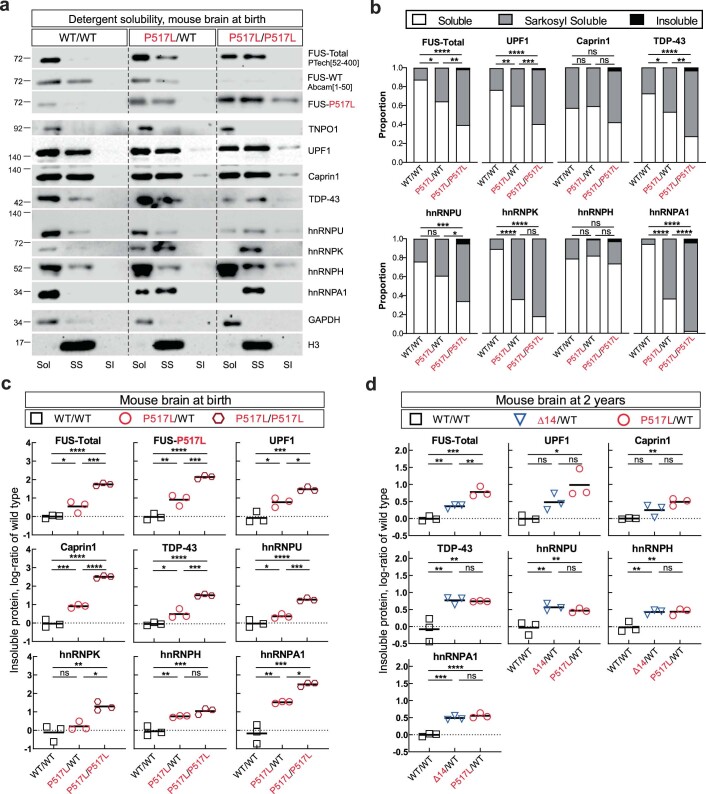
Extended Data Fig. 4. Detergent insolubility of mutant FUS and related RNA-binding proteins.
(a) Immunoblot of sarkosyl solubility fractionation of brain from newborn FUS WT/WT, P517L/WT, and P517L/P517L mice. Sol = soluble (in hypotonic buffer), SS = sarkosyl soluble (in 1% sarkosyl and high salt), and SI = sarkosyl insoluble fractions. (b) Quantitation of protein in Sol (Soluble), SS (Sarkosyl Soluble), and SI (Insoluble) fractions. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 comparing Soluble versus the sum of Sarkosyl Soluble and Insoluble fractions using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. N = 3 animals per group. (c) Quantitation of protein in sarkosyl insoluble fractions from newborn animals shown in Fig. 3c, expressed as log-ratio of wild type. (d) Quantitation of protein in sarkosyl insoluble fractions from 2-year-old animals shown in Fig. 3d, expressed as log-ratio of wild type. For c and d, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA with Tukey´s post hoc test. N = 3 animals per genotype.