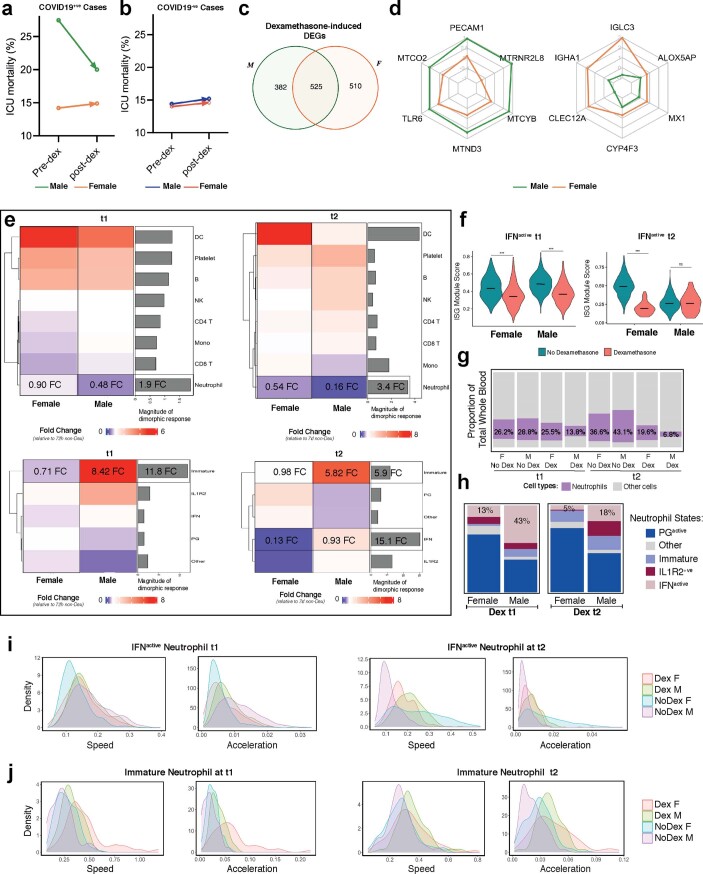
Extended Data Fig. 9. Dexamethasone attenuates neutrophil response in a sexually dimorphic fashion.
a-b. ICU mortality rates of sex-separated patients with (a) or without COVID-19 (b) comparing pre-dexamethasone (January 2020 till May 31st, 2020) and post-dexamethasone (June 1st, 2020, till May 31st, 2021) standard of care time periods. c. Number of genes that are uniquely or jointly regulated with dexamethasone between males and females. d. Differential magnitude or direction of regulation within dexamethasone-induced DEGs jointly regulated by both sexes. e. Heatmap depicting dexamethasone-induced shifts in cellular composition at t1 and t2 and accompanying bar plots showing magnitude of divergence between male and female response. Dexamethasone-induced shifts in neutrophil state composition at t1 and t2 along with magnitude of divergence between male and female response. f. Module score of ISG signatures in ISG-active neutrophils across sex and dexamethasone treatment at t1 and t2. Statistical significance was assessed using an ANOVA test followed by bonferroni-corrected two‐sided pair-wise t-tests. * p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.001; ns p-value > 0.05. Absolute p-adjusted values are provided in Supplementary Table 8. Center line indicates median data point. g. Comparison of proportion of neutrophils in whole blood samples from sex-separated cohorts. h. Comparison of neutrophil composition across sex in dexamethasone-treated patients at 72 hours and 7 days post-ICU admission. i-j. Histograms depicting dynamo-calculated distribution of cell speed (length of velocity vectors) and acceleration (subspaces where velocity undergoes dramatic changes in magnitude or direction) of all IFN-active (i) and immature (j) neutrophils, separated by sex and dexamethasone treatment for both t1 and t2.