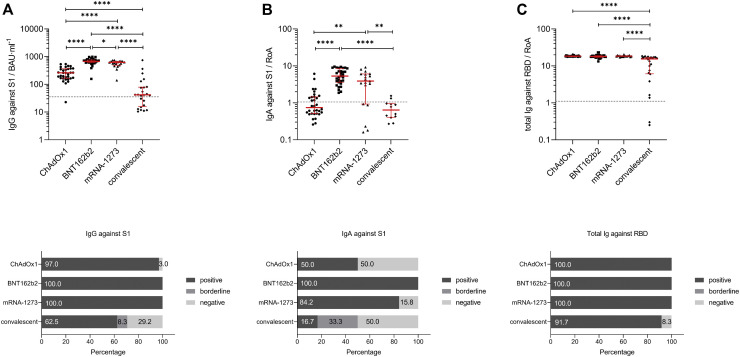
Fig 1.
SARS-CoV-2 antibody titer analysis using sera from fully vaccinated (ChAdOx1, BNT162b2, or mRNA-1273) or convalescent participants. A, Individual IgG antibody titer analysis against SARS-CoV-2-S1 domain for individuals fully vaccinated with ChAdOx1 (n = 33), BNT162b2 (n = 31), or mRNA-1273 (n = 23) and of convalescent patients (n = 29) were assessed with the anti–SARS-CoV-2 QuantiVac ELISA (IgG) kit. Results are presented as binding antibody unit per milliliter of serum (BAU∙mL−1). Corresponding percentages of participants and patients with positive, borderline, or negative IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2-S1 are visualized in the graph.B, Individual IgA antibody titer analysis against SARS-CoV-2-S1 domain for fully vaccinated and convalescent participants was performed with the anti–SARS-CoV-2-ELISA (IgA) kit. Results are presented as RoA. Corresponding percentages of participants with positive, borderline, or negative IgA antibodies against SARS-CoV-2-S1 are visualized in the graph.C, Individual total Ig antibody titer analysis against SARS-CoV-2 RBD for participants fully vaccinated and convalescent individuals was performed with the Wantai SARS-CoV-2 Ab ELISA kit. Results are presented as RoA. Corresponding percentages of participants with positive, borderline, or negative total Ig against SARS-CoV-2-S1 are visualized in the graph. Statistical significance between the 4 groups was determined by Mann-Whitney U test for nonparametric distribution (∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001). Medians are visualized as red lines together with the interquartile range as error bar. Cutoff values are illustrated by the gray dashed line.