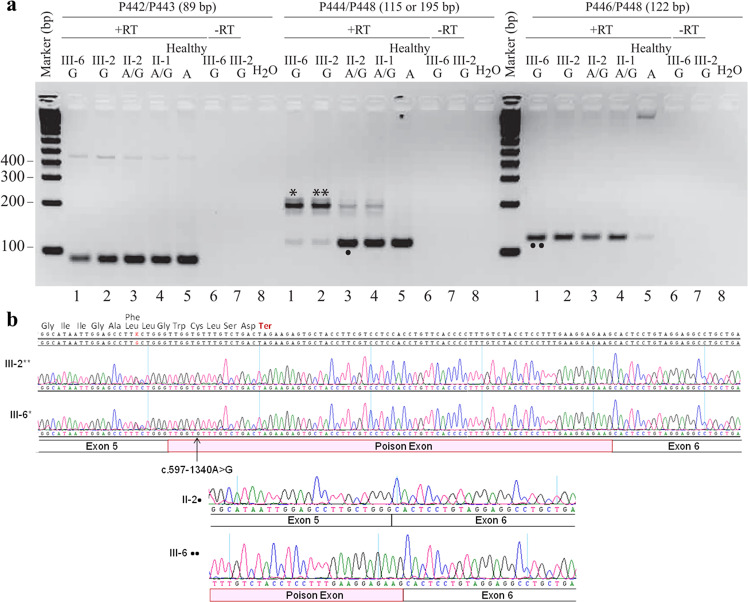
Fig. 6. TIMMDC1 c.597-1340A>G variant inserts an 80 bp poison exonic sequence between Exon 5 and 6 in TIMMDC1 mRNAs of the affected individuals.
a Agarose gel showing semi-quantitative RT-PCR amplicons from normally and alternatively spliced mRNAs from two affected (lanes 1 and 2), carrier parents (lanes 3 and 4) and an unrelated healthy control (lane 5) fibroblast RNAs. Minus RT reactions of the affected fibroblast RNAs (lanes 6 and 7) were also included. Left panel: Control PCR products from primers (P442/P443) located in Exon 3 and 4 showing amplification from the unaltered mRNA region, middle panel: PCR products from primers (P444/448) located in Exon 5 and 6 showing amplification of mRNAs with (lanes 1 and 2) and without (lanes 3–5) poison exon, and right panel: PCR products from primers (P446 located within poison exon and P448 within Exon 6) that specifically amplify mRNAs with poison exon sequence. Note that levels of mRNA with poison exon sequences in the affected individuals and parents (carrying the TIMMDC1 variant; lanes 1–4) are higher than the unrelated control (lane 5) that has low level of aberrant splicing that generates the mRNAs with poison exon sequences. See Fig. 2 for primer location. b Chromatograms showing mRNA sequences with an 80 bp poison exon in fibroblasts of the two affected individuals (see sequence of III-6*, III-2** and III-6•• bands from the gel in a). Parent II-2• band sequence, as expected, showed the absence of poison exon.